Jews in "Fertile Crescent" and Ur - deportation of 722 to Assyria - Mesopotamia - "Christian" influence and wars - Babylonian Talmud - creative period under pax arabica - silk trade - "Christian" violence - Jews spread over Russia - migration movements of racist Zionists against all Arabs - English Mandate 1920-1948 - migrations in Asia during World Wars - immigration into the war trap - emigration from China Communism
from: Encyclopaedia Judaica (1971): Asia; vol. 3
presented by Michael Palomino (2008)
| Share: |
Facebook |
|
Twitter
|
<ASIA.
History.
[Jews in the "Fertile Crescent" and Ur - commercial connections - sources]
Jewish history originated in this continent, in the Near-Eastern complex of the Fertile Crescent. The journeyings of the *Patriarchs led from *Ur of the Chaldees in present-day *Iraq through the crescent to *Egypt. In antiquity, *Canaan controlled the highway linking Asia with Africa (Egypt).
The Fertile Crescent had ties with Hellenic Europe. These were initially established through *Crete, and somewhat later through the contact with the *Philistines and *Phoenicians. Despite the many ties with Egypt, few traces of Egyptian cultural influence are found in *Erez Israel (Ereẓ Israel) [[Land of Israel]] of the biblical period. The effects of this geopolitical background are, however, clearly discernible. The cultural differences existing between the kingdoms of *Israel and *Judah and their separate destinies largely resulted from the exposure of the northern kingdom to influences emanating from *Syria, Assyria, and *Babylonia, and its commercial or other ties with the Asiatic area of the crescent.
[[See also: *Greece. There is another reason for the "few traces": according to Jewish archaeologists (e.g., Finkelstein and Silberman) these kingdoms - which are described in the Mose books - did not exist, or existed at another time, or in another way. From First Temple (of kingdom of David and Salomo) has not been found any peace, and from supposed Jerusalem of that time (kingdom of David and Salomo) has not found any peace either until today. A big part of the Mose books is invention and not historical, and much is missing. By there can have been a Jewish concentration in Palestine, but not a David and Salomo kingdom, and it seems that the Jewish center is more Ur than Palestine as it seams, also considering the following deportations and developments when Jews were brought back to the Ur region]]:
[Deportation to Assyria in 722 - developments of Jewry in Mesopotamia]
After the Assyrian conquest of the northern kingdom of (col. 739)
Israel in 722 B.C.E., masses of its population were deported further into the Asian interior
[[where - according to 1st Mose - the Jews originally came from, the region of "Ur". Then - according to word relations - a part of the deported Jews were deported to Pakistan and Afghanistan (to colonize this landscape) and became Muslims there, see the book: Jesus lived and died in Kashmir]].
With the Babylonian conquest of Judea in 586 B.C.E.., the transference of the center of Jewish life to *Mesopotamia was momentarily almost complete. Some historians believe that *monotheism crystallized in its pure form in Judaism from the impact of the Babylonian exile and the close confrontation with Babylonian paganism. Manifold religious and cultural concepts, the nomenclature of the months, the so-called Assyrian characters of the Hebrew script, were acquired in Mesopotamia and carried back to Erez Israel (Ereẓ Israel) [[Land of Israel]].
During the Second Temple period
[[according to Jewish archaeologists this temple is the only one, see Finkelstein-Silberman: The Bible Unearthed]]
these became central and integral elements in Jewish mores, thought, and literature. A large proportion possibly the bulk of Jewry stayed on in Mesopotamia after the Return to Zion, often in flourishing trade centers such as Nippur. Thus Babylonia also became a Jewish national cultural center.
[[It may be asked why the region of "Ur" did not become the center for the future. But since the Mose books were written the Jewish center is said to be Jerusalem and not Ur is not understandable. This would shift the Jewish center into a greater landscape and would give them more room...]]
["Christian" European influence on Jewry and wars]
On the other hand, European influences began to penetrate Jewish life and culture with greater force after the conquests of *Alexander the Great. These emanated from Seleucid Syria in the north, as well as from Ptolemaic Egypt in the south. When acculturation was pressed by forcible measures under the Seleucid *Antiochus IV Epiphanes, the sharp Jewish reaction culminated in the *Hasmonean revolt. Jewish influence on its part was evident in some of the Asian principalities. The royal house of *Adiabene adopted Judaism. The Hasmonean revolt was the only instance of a religio-national uprising by an Asiatic society against Hellenistic domination. In the protracted Roman-Byzantine period (63 B.C.E.-641 C.E.) Jewish resistance to alien domination continued, erupting in the Jewish War of 66-73 and subsequent revolts (see History of *Israel, Second Temple Period; *Bar Kokhba). The Jewish image and the horizon of the Near Est influenced the European conception of Asia until the modern era.
[Jewish development in Asia - Babylonian Talmud from Babylonian Jewry]
The Babylonian Jewish center, however, continued to develop independently under Arsacid Partho-Persian rule. The Jewish area of settlement expanded into Persia and toward Central Asia. Jewish settlements on the borders of the Roman and Persian empires in Asia developed a vital Jewish communal life and culture. Evidence of their exceptionally resplendent synagogue art is the *Dura-Europos synagogue and its paintings. The most important contribution of the Babylonian center for subsequent Jewish culture was evolved in the environment of the restored Sassanian Persian Empire.
The Babylonian *Talmud exerted its powerful influence on Jewish life on all subsequent generations. Thus Sassanian cultural and folk elements absorbed into the Talmud were integrated into Jewish culture in addition to the former Babylonian and early Persian accretions.
[Arab rule and "outstandingly creative period in Jewish history" - "pax arabica" - Jews coming up to China by silk trade]
The Arab conquest of Erez Israel (Ereẓ Israel) [[Land of Israel]], Mesopotamia, and the adjacent areas in the seventh and succeeding centuries [[the Arabs were fighting on fast horses - the loosing kings of Middle Asia had only slow elephants]] brought the whole of North Africa, and for a time *Spain, within the sphere of influence of the Muslim caliphate. The fact that its center of gravity and seat of government lay in the Fertile Crescent (*Abbasids, *Umayyads, *Damascus) had an incalculably important effect on Jewish life for generations. The Mesopotamian scene under Arab rule centering on *Baghdad formed the background for an outstandingly creative period in Jewish history.
This was the age of the *exilarchs and *geonim [[Talmud interpreters of the Jewish academies, religious leaders]], lasting approximately from the seventh to the eleventh centuries. Meanwhile, the pax arabica enabled the area of Jewish settlement to extend increasingly farther eastward. The commercial and industrial revolution of the ninth century gave particular impetus to this advance. Trade with *India, where Jewish communities existed perhaps as early as the fifth century, was a regular traffic in the geonic period. The ancient (col. 740)
Jewish settlement at *Kaifeng in China apparently owed its origin to the flourishing silk trade in about 1000. Jewish travelers of the 12th century. *Benjamin of Tudela and Pethahiah of Regensburg, reported dense and flourishing Jewish populations in most of the Near-Eastern areas. Source evidence from the Cairo *Genizah
[[Genizah = store-room / depository in a synagogue for worn-out / used religious books and texts]]
mirrored the the diversified nature of Jewish international trading activities in the Indian Ocean in the 12th century. Links were established from the Near East and Egypt with the Far East via the staging post in *Yemen.
["Christian" violence brings Jewish communities in danger - stable development under Arab rule]
The violence surrounding the *Crusades and the Tatar invasions of the 13th century critically endangered the Jewish communities throughout western Asia. In Erez Israel (Ereẓ Israel) [[Land of Israel]] many Jews were massacred, and after the 11th century the Jewish settlement there stood in need of constant replenishment by immigration from the Diaspora.
In the 13th century Mesopotamian Jewry was also almost annihilated though a remnant remained.Meanwhile the communities of Asia Minor had dwindled as a result of the traditional intolerance of the Byzantine rulers. However, a fairly robust Jewish society was flourishing in the areas comprised by the *Ottoman Empire in the second half of the 15th century. An isolated Arabized community of some numerical importance continued to exist in Yemen and the Arabian Peninsula, in conditions which remained unchanged for many centuries. In India the *Bene Israel of mysterious origin were settled in Bombay, in addition to the ancient communities in Cranganore (later transferred to *Cochin).
[Influx of Jewish refugees to Asia from Spain and Portugal]
An important reinforcement of the Jewish existence in Asia was provided after the expulsion from [[racist "Christian"]] Spain in 1492 [[and from racist "Christian" Portugal in 1498]]. The large numbers of Jewish exiles, followed later by Portuguese *Marranos, found new homes in various places within the Ottoman Empire [[above all in Constantinople, Greece and in Egypt]]. Their settlement was not confined to Ottoman territory in Europe, but also extended to Asia Minor, Syria, and other parts of Asia. The new immigration not only reinvigorated communities surviving from former days, but actually transformed their original character. Whereas these communities were formerly autochthonous, preserving the ancient native Jewish culture, they now assumed European characteristics. They became largely Spanish speaking and followed the Spanish rite. Probably the former Jewish traditions were genuinely preserved only in Persia, in the Yemen, and in the small surviving Jewish community of Iraq.
[[Often there were also two Jewish communities, an old Asian Jewish one, and a new Spanish Jewish one]].
The post-expulsion period also witnessed a revival of Jewish settlement in Erez Israel (Ereẓ Israel) [[Land of Israel]]. The neo-kabbalistic school of *Safed (see *Kabbalah) renewed Palestinian cultural and religious influences in Jewish life after a recession of many centuries. (col. 743)
[[It seems absolutely strange why the Mose books always refer to Jerusalem and not to Ur...]]
[Documentation of Jewish life in Middle Asia failing - Jewish creativity]
The record of Jewish life and creativity in Asia in the late medieval and early modern periods still awaits its definitive presentation. The state of research in modern Jewish historiography reflects its European focus. Numerically there was a Jewish decline in Asia and no certain data exist. Nevertheless the ancient matrix remained. In Yemen and in *Kurdistan Jewish creativity was manifested in specific folk art and customs. The national center of Erez Israel (Ereẓ Israel) [[Land of Israel]] drew to it devoted men and women in each generation. If the Asian communities failed to make their mark on European Jewry in the period, this was mainly the result of the general political predominance then achieved by Europe as a whole.
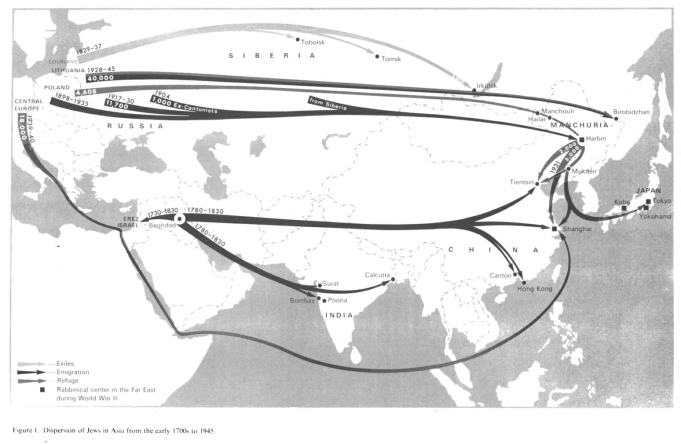
[19th century with migration from Central Asia to Far Asia - Jews reaching Central and Far Eastern Russia]
Two new waves of Jewish migration penetrated deep into Far Eastern Asia in the 19th century. Both were numerically small, but significant in their geographical scope and economic attainments. Both followed in the wake of eastward emigration from Baghdad and other cities in Iraq, mainly to areas in the British sphere of influence. Small communities that were established in India and farther east, in points as far away as Hong Kong, became extremely affluent and correspondingly important.
The second migratory wave to penetrate the fastnesses of Asia made the overland trek from Russia. Initially Jews went to live in *Siberia, mainly for trade for a limited period or when sentenced to exile. Others went on to *Manchuria, especially after World War I, and temporarily important communities were established in places like *Harbin. The industrialization of Asian regions of the [[criminal Gulag]] Soviet Union, and the development of scientific centers there, again stimulated Jewish movement to Asia. Despite its failure, the autonomous Jewish region of *Birobidzhan, created on Far Eastern soil, still harbours a Jewish community. (col. 744)
[Palestine with racist Zionist settlement fantasy and European Jewish money from Rothschild since 1880 - Balfour declaration of 1917]
In Erez Israel (Ereẓ Israel) [[Land of Israel]], however, new forces were at work. The Jewish awakening to *Zionism revitalized the Jewish settlement [[against the Arabs]]. After the 1880s the yishuv [[Jews in Palestine before 1945]] played a role of increasing significance in world Jewry, growing rapidly in numbers and developing a character and culture of its own.
[[This "development" in the desert against the Arabs was only possible by financial aid of banker Rothschild, because the racist Zionists were not at all loved by the Arabs, and since 1896 since the racist Herzl booklet "The Jewish State" was published the Arabs knew that racist Zionism wanted to enslave all Arabs - as the First Nations in the "USA" had been destroyed. Middle East conflict began in 1880 already when the Jews were given only desert for settlement, and when the Arabs boycotted these first "Jewish" settlements, and then Jewish European money flew in and the escalation went on and on...]]
Jewish settlement proceeded despite obstacles, and foundations were laid for state institutions. The achievements of the pioneers had their effect.
[[These "pioneers" were Jewish fighting terror groups against the Arab resistance, e.g., under racist Zionist leader Menahem Begin, criminal Haganah, criminal Mosad, making civil war against English rule and against the Arabs at the same time, setting up "over night settlements" etc. The foundations and state institutions were financed by Jewry of Europe and of the criminal racist "USA", e.g., by the Jewish Colonial Association (ICA), against the Arabs. And the racist Zionist "pioneers" were also working diplomatically]]:
By the *Balfour Declaration [[of 1917]] Erez Israel (Ereẓ Israel) [[Land of Israel]] became the declared Jewish national home. (col. 744)
[[This "Balfour Declaration" was a manipulation product of the racist Zionist "pioneers" on diplomatic paths in England. The definition of "National Home" was never specified. But reading the racist booklet "The Jewish State" the Arabs knew what were the racist Zionist ideas. Later the racist Empire English government wanted to keep a balance between racist Jewish Zionists and Arabs to hinder a big war and to preserve the oil connections with the Arabs]].
[Partly emigration from Turkey since 1919]
In the Middle East the reorganization of the Turkish state after World War I on nationalist lines and the changes in the Turkish economy had adverse effects on the local Jewish communities, which dwindled considerably. (col. 744)
[Mandate and Jewish "Ingathering" to Palestine 1920-1948]
From 1920, after the *League of Nations gave the mandate for Palestine to Britain, an entirely new situation was created. Within the next few decades after the creation of the State of *Israel in 1948, almost all the Jews of the historic communities of Syria, Lebanon, Iraq, and the Yemen had emigrated to Israel in the process of Ingathering of the Exiles. [[The Jews were brought to racist Zionist Free Mason CIA Herzl Israel 1948-1950]]. Only shadow communities remained. The new [[Zionist Free Mason CIA Herzl]] Israel also attracted numerous immigrants from other Asian countries, especially from those where economic conditions were poor, such as Turkey and Persia, as well as India. The "Black" Jews of Cochin, established on the Malabar coast from antiquity, migrated almost en masse. Scattered communities, however, continued to maintain (col. 744)
themselves here and there in the Asian continent. (col. 745)
[[The oriental Jews (Sephardim) were always "second class" Jews to the European Jews (Ashkenazim), the "first class" Jews. But the European Jews were taught by the oriental Jews (Sephardim) how old and of what kind old Jewry was. The "ingathering" was provoked by rising Arab anti-Semitism after the criminal foundation of the racist Zionist Free Mason CIA Herzl State of Israel without definition of borderlines. By the "ingathering" the Jewish connections around the whole world were given up and the racist State of Israel became fully dependent on Jewry of criminal racist "USA". The Arabs which - according to the racist Zionist Herzl booklet "The Jewish State" - have to be enslaved - work together with Russia and hinder the Jewish expansion for a Jewish Empire ("Greater Israel") from Nile to Euphrates (which is announced in 1st Mose chapter 15 phrase 18). Israel is without definition of borderlines and keeps the Herzl program as it's mental base saying that all Arabs should be enslaved and eliminated - as the natives in criminal racist "USA" had been eliminated. The eternal war trap of Middle East Conflict was born - and naive Jews coming to Israel in euphoria did not see this war trap. But would you like a neighbour state without definition of borderlines which plans to exterminate and to enslave you?]]
[1933-1945: Rising figure of Jews in Russian Asia and in Japanese occupied countries]
With the commencement of Nazi persecution, a considerable increase in the number of Jews in Russian Asia was reported, although the actual figures are not known. [[This was the Big Flight from Barbarossa, and by this many Jews could evade the Nazi Holocaust, but later lots of Jews were taken into the Russian army and died there]].
World War II completely changed the Far Eastern picture. Many refugees from the German-occupied countries and Russia escaped to territories under Japanese rule [[Big Flight from Barbarossa]]. The Japanese although introducing anti-Semitic measures, did not carry them out to the extreme. (col. 744)
[Emigration from Communist China since 1945]
The communist victory in China after the war made it impossible for the Jews to continue there in their former occupations. The recently established communities disappeared. (col. 744)
[[All flight and migration movements from Asia to Central and western Europe and to criminal racist "USA" are missing on the map. The Big Flight from Barbarossa is missing on the map, too (e.g. to Caucasus, Kazakhstan, by Caucasus to Iraq, etc.), and the emigration movements from Europe to Palestine are missing, too]].
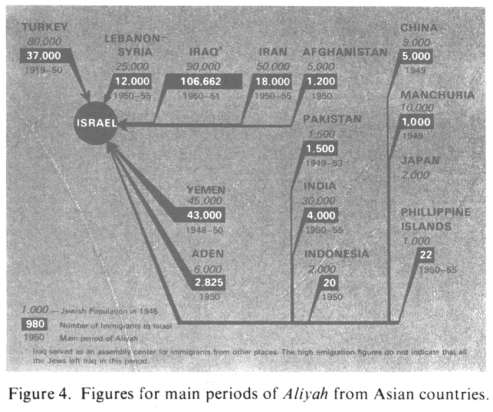
Table. Inner Asian immigration to racist Zionist Free Mason CIA Herzl Israel (aliyahs) 1919-1955
main period of immigration (aliyah)
Country
number of Jews in the country in 1945
number of Jews immigrating to racist Zionist Free Mason CIA Herzl Israel into the war trap of Middle East Conflict
xxxxxxx1919-1950xxxxxxx
Turkeyxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxx80,000xxxxxxx 37,000xxxxxxx 1948-1950
Yemen
45,000xxxxxxx 43,000xxxxxxx 1949
China
9,000xxxxxxx 5,000xxxxxxx 1949
Manchuria [[part of China since 1949]]
10,000xxxxxxx 1,000xxxxxxx 1949-1953
Pakistan
1,500xxxxxxx 1,500xxxxxxx 1950
Afghanistan
5,000xxxxxxx 1,200xxxxxxx 1950
Aden
6,000xxxxxxx 2,825xxxxxxx 1950
Indonesia
2,000xxxxxxx 20xxxxxxx 1950-1951
Iraq*
90,000xxxxxxx 106,662xxxxxxx 1950-1955
Lebanon-Syria
25,000xxxxxxx 12,000xxxxxxx 1950-1955
Iran
50,000xxxxxxx 18,000xxxxxxx 1950-1955
India
30,000xxxxxxx 4,000xxxxxxx 1950-1955
Philippine Islands
1,000xxxxxxx 22xxxxxxx [[?]]
Japan
2,000xxxxxxx [[?]]xxxxxxx *Iraq served as an assemble center for immigrants from other places. The high emigration figures do not indicate that all the Jews left Iraq in this period. table by Michael Palomino; from: Encyclopaedia Judaica (1971): Asia; vol. 3, vol. 746
[[The Jews who left Asia to other continents are not mentioned in this article]].
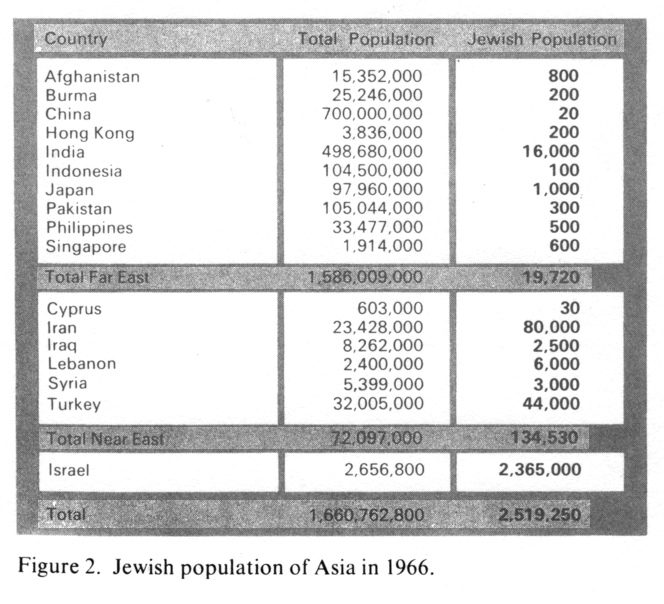
Jewish population of Asia in 1966
Encyclopaedia Judaica (1971): Asia; vol. 3, col. 743: Table. Jewish population of Asia in 1966
Country
Total Population
Jewish Population
Afghanistan
15,352,000xxxxx
800xxxxx Burma
25,246,000xxxxx 200xxxxx China
700,000,000xxxxx 20xxxxx Hong Kong
3,836,000xxxxx 200xxxxx India
498,680,000xxxxx 16,000xxxxx Indonesia
104,500,000xxxxx 100xxxxx Japan
97,960,000xxxxx 1,000xxxxx Pakistan
105,044,000xxxxx 300xxxxx Philippines
33,477,000xxxxx 500xxxxx Singapore
1,914,000xxxxx 600xxxxx Total Far East
1,586,009,000xxxxx 19,720xxxxx
Cyprus
603,000xxxxx 30xxxxx Iran
23,428,000xxxxx 80,000xxxxx Iraq
8,262,000xxxxx 2,500xxxxx Lebanon
2,400,000xxxxx 6,000xxxxx Syria
5,399,000xxxxx 3,000xxxxx Turkey
32,005,000xxxxx 44,000xxxxx Total Near East
72,097,000xxxxx 134,530xxxxx
[[racist Zionist Free Mason CIA Herzl]] Israel
2,656,800xxxxx 2,365,000xxxxx
Total
1,660,762,800xxxxx 2,519,250xxxxx from: Encyclopaedia Judaica (1971): Asia; vol. 3, col. 743
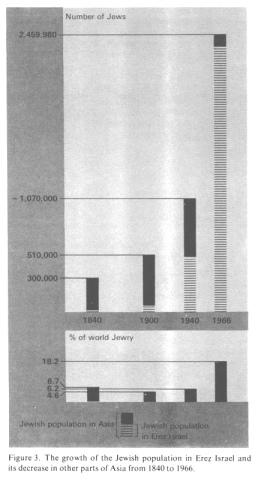
Encyclopaedia Judaica (1971): Asia, vol. 3, col. 745: Figure about the growth of the Jewish population in Erez Israel and its decrease in other parts of Asia from 1840 to 1966 [[going into the war trap of Middle East Conflict by euphoria]].
In 1970 there were 2,518,000 Jews in the [[racist Zionist Free Mason CIA Herzl]] State of Israel, forming about 15% of world Jewry and the third largest Jewish concentration in the world.
Demography and Statistics
The growth of Jewish population on the Asian continent during a period of just over 120 years, from 1840 to 1961, shows a steadily increasing tempo. This is, no doubt, in keeping with the general improvement in Asian health and hygienic standards, especially among urban populations, affected by the penetration of European civilization. In the first 60 years (1840-1900) the Jewish population increased by only 70%; over the next 40 years (1900-40) it more than doubled, and in the next 21 years (1940-1961) the figure almost tripled, mainly due to the increase of the Jewish population in Erez Israel (Ereẓ Israel) [[Land of Israel]].
The drop in the ratio of Asian Jewry to total world Jewry during the first 60 years stemmed from the fact that population increase in Asia lagged considerably behind that in other continents. But the situation changed in the 20th century, and more especially in the period 1940-61, when the percentage more than tripled that at the outset of the period. This percentage increase, however, was not due solely to the absolute numerical growth of the Jewish population in Asia, since it was conditioned in the main by the annihilation of European Jewry, which changed the relative scale. (col. 745)
Table 2 indicates that Jews constituted everywhere only a fraction of 1% of the total general population. About 100,000 Jews were scattered over this gigantic continent, outside of [[racist Zionist Free Mason CIA Herzl]] Israel, as minority groups engulfed by overwhelming and in the Arab countries, extremely hostile - majorities and are thereby seriously exposed to various dangers. Complete assimilation threatens Asiatic Soviet Union Jewry, dispersed over the vast expanses of Asiatic Russia, among which the rate of mixed marriages had been as high as 25-30% before World War II.
Bibliography
-- E.N. Adler: Jews in Many Lands (1905), 173-244
-- I. Cohen: Journal of a Jewish Traveller (1925), 105-266
-- S.S. Mendelsohn: Jews of Asia (1930)
-- J.J. Benjamin: Eight Years in Asia and Africa (1859)
-- J. Saphir: Even Sappir, 2 vols. (1866)
-- I. Ben Zvi: The Exiled and the Redeemed (1957)
-- Fischel, Islam
-- H. Lord: Jews in India and Far East (1907)
-- H. Dicker: Wanderers and Settlers in the Far East: a Century of Jewish Life in China and Japan (1962)
-- S. Strizower: Exotic Jewish Communities (1962)
-- S.D. Goitein: A Mediterranean Society, I (1967)
-- Neusner: Babylonia
-- AJYB: passim.
[ED.]> (col. 746)
^