pH value in the blood is controlled
with a blood gas analysis (BGA) [web01].
pH value in the blood is
always buffered between 7.35 and 7.45 in the
arterial blood [web04].
According to the sources the
definition of acidosis and alkalosis is a little
bit different but not much:
<A pH value higher than 7.45 is called
alkalosis (basic) and lower than 7.37 is called
acidosis (sour).> [web03]
(original
in German: <Ein pH-Wert höher als 7,45 wird
als Alkalose (basisch) bezeichnet und niedriger
als 7,37 als Azidose (sauer).>
[web03])
<Under 7.36 is an acidosis - on 7.44 or higher
the doctors speak of an alkalosis.> [web01]
(original in German:
<[...] unter 7,36, liegt eine Azidose
- auf 7,44 oder höher, sprechen Ärzte von einer Alkalose.>
[web01])
For urine and saliva pH7 is considered to be neutral
and there is more tolerance downwards considering
acidity.
pH value in the blood in healthy
bodies is always the same pH7.35-7.45 [web01] resp.
it is around 7.4 [web01] and is buffered. Here is a source about that:
<pH value of the blood is buffered by a complex
buffering system of solved carbon dioxide, salts and
proteins, the so called blood buffer. Normally pH
value in the arterial blood is between 7.35 and
7.45.> [web04]
(original in German:
<Der pH-Wert des Blutes wird durch ein
komplexes Puffersystem von gelöstem
Kohlenstoffdioxid, Salzen und Proteinen, dem sogenannten Blutpuffer, eingestellt.
Normal ist ein pH-Wert von 7,35–7,45 in
arteriellem Blut.> [web04])
In the blood there is no big tolerance. The "right"
pH value in the blood is between 7.35 and 7.45;
under pH7.35 the condition is sour (acidosis,
overacidification), and over pH7.45 this is a basic
alkaline condition (alkalosis, underacidification)
[web05].
pH value in the blood with new born babies is
differing a little bit and after 2 days is stable:
New born baby 1st day: pH7.20-7.41
New born babies 10 to 90 days: pH7.34-7.45
Little child 4-12 months: pH7.38-7.45 [web05].
pH value in the blood 7.35-7.45 - optimal
immune system
-- immune system is working in an optimal way
-- illnesses are blocked from the beginning
-- infection risk is very low [web06].
pH value in the blood is regulating
- <sugar metabolism (glycolysis)
- muscle activity and the distribution of
excitation in the heart
- vessel resistance
- forming of oxygen of the blood by the red blood
colorant (hemoglobin).> [web1]
Measuring pH value after accidents is rated as an
important indicator for illnesses or troubles [web01].
When there is a lung disease
(respiratory trouble) the body is trying to arrange
pH value in the blood by kidneys and liver. In other
cases when there is an organic failure (non
respiratory trouble) the body is trying to balance
the situation with the lungs [web02].
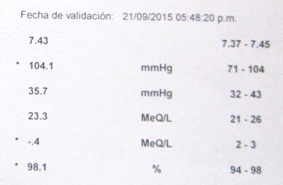
A report with a pH value of 7.43
On September 21, 2015 a laboratory in Lima measured my
pH of my blood: I had pH7,43 in the blood:
 Lab report of
Suiza Lab in Lima from September 21, 2015 with a
pH value of 7.43 in the blood
Lab report of
Suiza Lab in Lima from September 21, 2015 with a
pH value of 7.43 in the blood
Illnesses causing a too sour pH value in the blood
under pH7 (acidosis) are:
-- <lung diseases and troubles with oxygen exchange
-- heavy brain diseases (brain tumor or meningitis
etc.) provoking a respiratory paralysis hindering
oxygen exchange
-- big diarrhea loosing many basics
-- concentration of acids in the body (diabetic
ketoacidosis, metabolic disorder etc.)
-- kidney diseases (kidney insufficiency)
-- mistake during a blood transfusion> [web03]
Illnesses of airways (respiratory troubles) which are
provoked by a too sour pH value (acidosis) are for
example:
-- <a change of airways or a block of gas exchange
in the lung e.g. with a pulmonary edema ("water in the
lung")
-- a pneumonia
-- loss of working lung tissue (e.g. with
tuberculosis)
-- an insufficient breathing mechanism (e.g. with an
intoxication with sleeping pills)
-- a paralyzation of muscles of breathing (e.g. with
polio)
-- a dysfunction of breathing reflex.> [web17]
More illnesses provoking too sour pH values (acidosis)
in the blood, here are examples:
- <weak kidney or kidney failure (excretion of
acids is not working enough)
- metabolism diseases like Diabetes
mellitus (acids are concentrated in
metabolism)
- heavy bodily work or lack of oxygen (lactic acid
is concentrated in metabolism)
- long lasting diarrhea (excretion of bases is too
much)
- some intoxications.> [web02]
A sour pH value in the blood (acidosis) can provoke
the following illnesses - here are examples:
- <higher blood glucose (high blood sugar
(hyperglycemia)
- potassium flows from the cells, and in the blood
the concentration is increasing (hyperkalemia)
- excitations of the heart are derived only slowly
- cardiac arrhythmia can come
- force of the heart is sinking, and the vessels
are broadening
- there is the danger of a loss of blood pressure
- brain pressure can rise
- the affected person can be unconscious.>
[web2]
Possible illnesses when pH value in the blood is
too basic alkaline (alkalosis) with a pH of over 7.5
From pH7.44 the pH value in the blood is rated basic
alkaline [web01]. Symptoms for this alkaline blood
levels (alkalosis) are for example:
- <lower blood sugar (hypoglycemia)
- potassium is flowing into the cells and in the
blood the concentration of potassium is sinking
(hypokalemia)
- cardiac arrhythmias occur
- convulsions can occur.> [web02]
Illnesses which are provoking a
basic alkaline pH value in the blood of over pH7.5
are:
-- too much oxygen supply by a too intensive
breathing (hyperventilation) [web03] because of
stress or excitation, too many acids are excreted by
the lung provoking a "respiratory alkalosis" [web01]
-- inflammation of the brain with an irritation in
the brain's breathing center [web03]
-- continuing vomiting with the loss of stomach acid
[web03]
-- troubles with the balance of hormones (Cushing's
syndrome with too much cortisone production etc.).
[web03]
For bringing back the pH values to the positive zone
one has to eliminate the causes, e.g. to heal an
infection [web02].