Chapter Two: The Commodity, part 1
Part 1: 1: reasons for prostitution - 2: discriminating and downgrading of women in Asia - 3: daughters are taught a feeling of 'duty' - 4: Asian women are a prestige for the Asian husband - 5: pregnant and raped Asian women have to go to the brothel - 6: more discriminations of Asian women - 7: facade and reality about sex life in Asian society
Help for widows by Aim Asia network in India [6]. Why the Asian governments cannot install such social networks by themselves?
Because there is hardly any reliable bank or mail system in the Asian countryside, and widows often cannot read nor write...
by Louise Brown
presented and with subtitles by Michael Palomino (2013)
| Share: |
Facebook |
|
Twitter
|
2.1: General indications about reasons for prostitution
General indications: Profits in the prostitution business - poverty in Asia [in the countryside] drives women into prostitution
For poverty the Asian governments are responsible not installing social networks and not installing good jobs in the countryside - and not making propaganda for contraceptions or not having certain good contraceptions in the country like hormone ring, the best and easiest contraception a woman can have. But many governments do not read new things and in Asia most government members are not interested in Internet and cannot even handle Internet - and that's why hormone rings are not to have in Asia or Central and South "America". This is one more part of the Asian mess...
Vagina ring, hormone ring, from "Nuva Ring" [1]
Prostitution pays. It profits many people - but not necessarily the girls and women whose bodies are sold. For some of Asia's poorest families, sending a daughter into prostitution makes the difference between absolute poverty and having just enough money to survive on a tiny and increasingly less fertile patch of land. For some women prostitution is the only way to survive in a world of limited options. Sex work has few competitors in terms of earning power for the badly educated and the unskilled. Some women choose to become prostitutes because of these financial rewards, but most women have no option. They are reared in poverty, socialized amid discrimination and conditioned to accept narrow choices. They are not exercising their right to 'choice' in entering sex work. They are vulnerable, and this vulnerability, together with their sexuality, is commodified and commercialized so that they can be traded on the sex market.
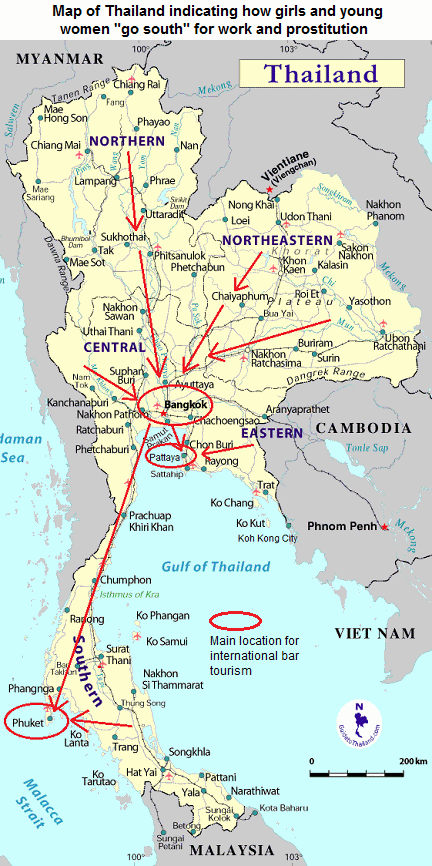
Thailand with poor north driving girls and women into prostitution
The link between poverty, prostitution and the trafficking of females is complicated. I want to be very clear: prostitution is not (p.29)
just a product of poverty. In more developed countries like Thailand poverty is no longer the driving force in the entrance of young women to prostitution. In northern Thailand prostitution is a career option for many young girls. If they are successful they will be able to buy a house and consumer goods and the respect of their family and neighbors. Many prostitutes are poor but their poverty is relative and not absolute. If prostitution was simply about poverty we could have expected a contraction of the sex industries in countries with fast-developing economies.
Supplement: Poverty without education - and career risks at the bar
Map of Thailand indicating how girls and young women "go south" for work and prostitution
Poverty in Chian Mai, northern Thailand [2]
First one has to know: in the countryside of Asia there was mostly on telephone, and today there are mobile phone systems but mostly there is NO Internet. And this makes this population very curios but also anxious.
Making money in the prostitution business is not so easy as writer Louise Brown is describing it as "a career option for many young girls".
-- First the Thai girls from the countryside don't speak English well and when there are international tourists or mafia customers they often don't understand each other at all but the girls and young ladies can be victims of anything.
-- Second point is that mafia networks are working very badly in Thailand and there is not only Thai mafia, but above all right wing extremist German, Swiss, Russian and English mafia working in Thailand with any danger of kidnapping or extortion.
-- Third point is that girls in the countryside in Asia are often educated with much alcohol (on rice farms during the rainy season they are working 6 months and during the dry season they are drinking alcohol 6 months until no money is left...), and when the girls go into prostitution this is often connected with even more alcohol and eventually also with drug abuse for euphoria in the bar (which is paid by the customers). Thus at the end there can be some money left and sent home and a new house but no brain is left because of the huge alcohol consumption: capacity of memory is often lost and capacity of evaluation and assessment is lost too therefore life cannot be arranged well any more and the person ends as a nursing case and is even ridiculed (this also happens with many government members in Asia loosing any competence and intellectual power also in the upper police grades and that's why Asia is socially so desorganized, corrupt and dependent from foreign mafia groups which are less alcoholic...)
-- Fourth point is that the girls or young women are loosing much money with own alcohol consumption or spending much money for clothes and jewelries which can also be stolen or lost - thus there is hardly any money at the end. Thai girls and young women in the countryside simply have no economical education and will not learn it in a bar either. Therefore such a career should only last 5 years and then the job should be a non alcoholic one. But many are doing it up to the "bitter end"...
-- The last point of danger in prostitution business in Asia are corrupt police commanders arranging "cases" as they want when help is needed and also manipulating girls and customers so the girls are always dependent on the police commanders and eventually have to serve them or are bribed by them when they serve them. This concerns not only Thai police commanders, but this concerns also translators in tourist centers like Pattaya and Phuket "indicating" to Thai policemen what is to do when there is a conflict with international tourists or "normal men" so the corrupt "translator" from certain foreign mafia groups (e.g. from criminal Swiss and German or Russian mafia groups in Thailand) is determinating the work of the Thai police - only because Thai police does not speak English well and has no stand but is dependent on the translators forever. This also counts for any other poorer Asian country...
-- And of course the girls and young women from the countryside have no education program in the town where they are working at bars and in brothels. They don't learn anything during all these years. Mostly they don't know what is the mouse of a computer, how Internet is working or where to look for an interesting book. The only strategy is drink - fuck - and money - and all is payed by the customer. And mostly they want to stay like this until they loose their brain because alcholic beverages are eliminating the brain partly, and they are often also losing their feminine and soft voice because the alcoholic beverages are destroying the vocal chords. But they don't know about these two losses but they want to feel good with their money. Principally they only feel good at home in the countryside - where is no Internet. Government is not working either. This counts also for any other poorer Asian country, not only for Thailand...
Expanding Thailand, Philippines, Malaysia and Indonesia - education of girls for prostitution in rural parts of Asia
But during the 1980s and 1990s the sex industry in countries like Thailand, the Philippines, Malaysia and Indonesia expanded as the standard of living of large sections of the population improved. There are many poor communities and families who would never send a child into sex work. I am afraid, however, that there are an increasing number who encourage and sometimes force daughters into prostitution. In some rural parts of Asia the breeding of girls for prostitution has become a kind of lucrative cottage industry [1].
[1] John Frederick: Reconstructing Gita; In: Himal; vol. 11, Nº 10, October 1998
Girls come often from poorest regions - from poorest families - from minorities - with bad education
All women in Asia are discriminated against relative to men within their own social and economic classes. But this does not mean that all women are equally burdened by the weight of discrimination. The girls who find themselves trapped in the worst kind of prostitution are not from privileged families, nor are they from middle-class families. They come, almost invariably, from the poorest communities and they are often from ethnic minorities. In South Asia they are from untouchable castes and scheduled tribes and, almost without exception, they are very badly educated [they don't speak English!]. They are exploited in the worst forms of prostitution for the simple reason that it is easy to exploit them. They are the poorest and most vulnerable members of largely powerless communities.
Old traditions in Asia - women seen as the property of men
Both traditional and modern Asian societies are highly gender based. This is changing in economically advanced Asia but even here the improvement in women's status is won at a price and, lie in the West, old forms of discrimination are being reformulated to (p.30)
preserve the sexual privileges of men. In many parts of contemporary Asia women are seen as the property of men. A woman finds a role in society and is validated by her relationship with a male: first with her father, then with her husband and later with her son. A complex mix of religion, cultural practices and economic discriminate against women.
System 1: daughters are unwelcome: dowry to marry her off is legal - the daughter leaving the family when she could be a useful person
In most parts of poverty-stricken South Asia the birth of a daughter is unwelcome because a female is considered to be an economic liability. The evil of dowry is fundamental to this: families pay for girls to be married and the status of the match is intimately related to the size of the dowry. In countries like Bangladesh where dowry was not traditionally common, the practice is now spreading rapidly [2].
[2] Sarah C. White: Arguing With the Crocodile: Gender and Class in Bangladesh (Dhaka: University Press, 1992), pp. 102-107
And in societies in which it is customary, dowry prices are escalating. The financial problems of giving birth to a girl child are therefore being magnified.
Payment of dowry is a duty that cannot be shirked if a daughter is to make a respectable marriage and thereby to add to the prestige of the family. Upon her marriage the girl then becomes the property of her husband's family. So not only does a girl's family have to feed and raise her but they also have to pay a substantial sum to marry her off. Just at the time that she becomes a useful economic addition to the family, she is transferred to another household, and her husband's family then own and profit from her labor. It is with good reason that a girl in South Asia is often described as a 'guest in her father's house'.
System 2: daughters cost a bride price - trade of girls and women is legal...
Not all communities in Asia pay dowry. Some pay bride price - which is a payment made by the bridegroom's family to the parents of the girl. In theory this sounds like an improvement upon the dowry system and, in some ways, it is. At least it acknowledges that a female has some value and it has some impact upon the way that girls are treated. Bride price, for example, is paid in tribal areas of Pakistan. Here a girl is seen as a financial asset and it is in her family's interests to take care of her and feed her well until she marries [3].
[3] Khawar Mumtz and Farida Shaheed: Women of Pakistan: Two Steps Forward, One Step Back (London: Zed Press, 1987), p.27
No prospective husband will pay handsomely for a thin, (p.31)
overworked and unhealthy wife. Yet, at the same time, this practice is only the lesser of two evils because bride price implicitly recognizes that a female is a commodity to be traded.
System 3: no dowry - no handsome man - or no marriage at all
For those who cannot pay dowry the options are a marriage with an unpromising husband or no marriage at all.
System 4: stepmother torturing the stepdaughter - and no money for a marriage - the girl is sent for work
A sixteen-year-old prostitute in a Calcutta brothel explained how she had arrived in the city from an impoverished Bangladeshi village the year before.
<My mother died three years ago and my father married again soon after. My new mother didn't want me ... especially when she had a new son. And my aunts and uncles didn't want me either because no one wanted to have the expense of marrying me. So I was sent to the city to find work. That way they said that they wouldn't have the cost of feeding me either.>
'Missing' women in Asia
Millions of women are 'missing' from India's census because they were either aborted, killed at birth or because they died from neglect as children. In South Asia as a whole it is estimated that seventy-four million women are 'missing' [4].
[4] Mahbub ul Haq: Human Development in South Asia 1997 (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1997), p.23
2.2: Discrimination of women in Asia downgrading them systematically
[What does this downgrading mean? This means that women do bad work or are suffering diseases and are not claiming anything. But sometimes they are also downgrading themselves...]
China discriminating girls
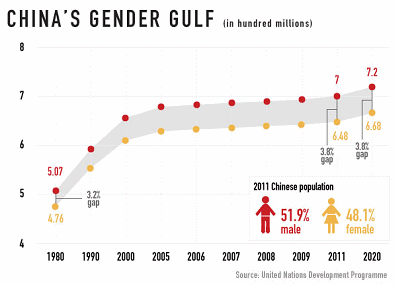
In China too the sex ratio is unbalanced. In 1979 the Chinese government instituted a 'One Child Policy' in an attempt to control the country's demographic explosion. The policy was extremely successful but it had an unintended side effect: if couples were allowed to have only one child they wanted a son, who was considered far more valuable in the eyes of society than a daughter. Ten years after the policy was implemented 114 boys were born - and registered - for every 100 girls [5].
[5] China Data Center, University of Michigan, 1998. Figures are taken from China's National Bureau of Statistics.
Female infanticide has a long-honored tradition in China and the One Child Policy has done little to eradicate it.
Supplement: Details about Chinas ratios with men and women
China, relation between men and women from 1980 to 2020, graphics [4]
It seems incredible what happens in China: genetic diagnostic can say after 4 weeks of pregnancy if the fetus is male or female and then many female fetus are killed because a son is wanted. Thus in China the natural relation between man and female with 51% female and 49% male children is turned in the other way round and the result are about 52% men and 48% women - provoking more prostitution, and poor women (e.g. from Vietnam) are coming to China for prostitution or for marriage business.
Asia is discriminating women systematically
In all parts of Asia girls are less highly valued by society. The situation is most acute in the poorer, least developed parts of the region. South Asia has some of the worst gender development indicators in the world and here girls are discriminated against from the (p.32)
moment of their birth [6].
[6] Haq: Human Development in South Asia 1997, p. 20-24
They are given less care, less love, less food and less medical attention than their brothers are. Middle Eastern countries are usually assumed to perpetrate the worst abuses on women, but a glance at gender-related statistics indicate that it is Pakistan that wins the award for the most extremely women-hostile society. Its female literacy rate is only 23% compared with 49% for men. Among children aged between one and four, the female mortality rate is 12% higher than male mortality. Women's share of paid economic activities, their access to senior administrative and managerial positions, and their representation in the national parliament are all minimal [7].
[7] Haq: Human Development in South Asia 1997, p. 21-22, 40-41
To be a woman in South Asia is to be, in the words of a respected Pakistani economist and social commentator, 'a non-person'. [8]
[8] Haq: Human Development in South Asia 1997, p.20
[Discrimination between men and women in South Asia can be described with an example of Vietnamese culture where fathers are sleeping with the sons in the front room and women have to sleep with the daughters in the back room. The book "Culture Shock" by Claire Ellis describes it like this:
<Traditionally, the father and sons sleep in the front of the house with the ancestral shrine and the daughters and mother sleep in the back (considered the lower) part of the house. This arrangement in itself helps to control the birth rate!> [web02]
Modern laws for women rights exist - but are not realized - Chinese communism failed also with right for women
Children and women are considered to be the possessions of the traditional Asian family. In many countries legal frameworks have enshrined the rights of ethnic minorities, low castes and women, but the enactment of laws has not altered deeply seated cultural prejudices. The example of China is instructive. After the triumph of the communists in 1949 China attempted to remove sexual discrimination, polygamy, prostitution and the sale of women. On paper this looked like magnificent and successful effort, but old practices persisted despite the propaganda. And, once the control that the Communist Party exercised over the economy was relaxed a little in the late 1970s, those ingrained behaviors returned. China buys and sells its women and girls today in much the same way as it did a century ago. Only now it does so in the name of the free market.
Women have a 'second-class status' - women can rise their status only by marriage - women excluded from rights of property and inheritance, from jobs
Women and girls are treated as property because they are dependent upon men economically and socially, and because they have very few opportunities to build a life outside the confines of the family. Girls are socialized to accept their second-class status and to look for validation from a man. Many take this to be entirely natural. Marriage for most women in Asia is the principal means to a livelihood and social status. In some parts of less-developed Asia (p.33),
like in Nepal, women are denied basic property and inheritance rights, and they are excluded from jobs that can pay a living wage. This is changing in the developed countries of the region as women gain access to well-paid employment outside the home. And even in the poorest countries it is also changing - but it is doing so slowly.
[Reasons for poverty
Writer Louise Brown never indicates why poverty exists: because governments want this poverty:
1: not installing social networks
2: nor installing good jobs in the countryside
3: nor making available easy contraceptions like the vagina ring or hormone ring in the countryside].
2.3: Daughters in Asia are often taught a feeling of 'duty' for their families
Feeling of 'duty': Thailand: girls have to pay back their 'breast milk money' by caretaking family members - Philippines: girls have a 'debt of gratitude' - China: children have a 'debt for giving them life'
In Thailand daughters are cast in the role of caretakers of the family. As in the rest of South-East Asia girls are expected to pay back their 'breast milk money'. In the Philippines girls are obliged - at least psychologically - to pay their utang na loob (debt of gratitude) to their parents. Children of Chinese families are in their parents' debt for giving them life [9].
Thai Mother from Paudung minority nursing baby [5]. For this nursing daughters should feel "guilty" having a "duty" for their families. Crazy Asia...
[9] Marjery Wolf: Women and the Family in Rural Taiwan (Stanford, California: Stanford University Press, 1972), p.14
Feeling of 'duty': drive of daughters to prostitution for their family: Nepal, Indonesia, Philippines, Thailand, India, southern China
Feelings of duty and the desire to look after parents are fundamental to a caring society. But for some families, driven mostly by poverty but sometimes by greed, there is no limit to what these obligations can entail. In areas where prostitution of girls is well established, families may expect pretty daughters to enter prostitution. In areas of Taiwan there is a tolerant attitude to women supporting parents through prostitution [10].
[10] Wolf: Women and the Family, p. 207-208
Exactly the same holds true for prostitute-recruiting grounds in Nepal, Indonesia, the Philippines, Thailand, India and southern China.
Feeling of 'duty': the power of the family as 'protector' - girls can be victim of failing families
Families provide protection but they can also be a prison in which the worst abuses take place. This is a universal truth. But for the abused and exploited child in Asia there are few avenues for escape precisely because the family is accepted as the ultimate protector of women and children. The counterpoint to this is that girls become easy prey when families fail. The family is the protector of a woman's virtue. There is no protection for the girls whose families fail them. There is no economic security and no social status. When they do not belong to one man they belong, by default, to all. Women like these constitute a large proportion of the prostitutes of Asia.
Reasons for adult women to become prostitutes: being widows, divorced, deserted, left alone with children - and family is no 'protector' any more
It is a myth that the Asian family always looks after its own. Red light areas in South Asia are filled with a large proportion of women who have been widowed, divorced, deserted and left with young (p.34)
children to feed and clothe. These women have not received support from their own or their husband's families and so they have been doomed to a life of prostitution. Likewise in South-East Asia a significant number of prostituted women are unmarried or divorced mothers who have no other means of maintaining themselves and their children.
[For these cases social networks are missing in Asia: rent for widows, support for divorced women, women left alone with children. The Asian governments DON'T feel ANY "duty" whereas since 20 years Minister of Family, Minister of Education or Minister of Culture are WOMEN!]
Help for widows by Aim Asia network in India [6]. Why the Asian governments cannot install such social networks by themselves?
Because there is hardly any reliable bank or mail system in the Asian countryside, and widows often cannot read nor write...
2.4: Women in Asia for the prestige of the husband
Women as social link of families - enrichments or slavery in the family - divorce is not allowed
Women may be second-class citizens but paradoxically they are also vitally important. This importance goes beyond sustaining the family and giving birth to, and raising, a new generation. Women are signifiers of community and of hierarchy. All societies are hierarchical, and Asian societies are deeply hierarchical in a very formal sense. One of the principal means by which men denote these hierarchies is in the control of and access to women.
Women are exchanged in marriage. This means that marriage signifies the binding of two families rather than simply two people. It is an economic and social contract. Of course women can benefit from this. At the best of times they gain economic security and social status. But they can also suffer terribly because they are part of a transaction. They are commodities, and to be valuable commodities in the marriage market they must have had no previous owners.
Women for Asian men as prestige objects and for fun: 'good' or 'bad' women - 'decent' women (have to be virgins) or 'whores' - Asian men use both
Virginity and chastity are central to the dominant strands in Asia's value systems. A Korean proverb which says that 'chastity for a woman is more precious than life' [11]
[11] Cited in Moon: Sex Among Allies, p.40
sums this up perfectly. The typical model is remarkably similar to that of middle-class Victorian England in which there were 'good' women and 'bad' women. It is another version of the whore / Madonna divide so central to Christian thought. This distinction between women has almost universal applicability because it is universally useful as a means of controlling women by granting men the right to label them as 'decent' or as 'whores'.
First, there are the good women. These are the women whom men marry: they are good wives and dutiful daughters; they are the females a family can exchange to enhance its social status. Then there are the bad women. These are the prostitutes: the (p.35)
ones seemingly outside the family system [and Asian men are laughing at them but using them]. They are not owned by an individual family, or by an individual man. In this way they can be used by all. The existence of this group of women means that men can be assured of having sex with multiple partners even in a society in which women's sexuality is rigorously policed. And all this is achieved without having to disrupt the harmony of their own tightly structured families or those of other men.
A girl who has lost her virginity is irredeemably [without hope] altered [changed]. Within marriage, defloration is a symbol of a husband's possession of his wife. It is a travesty for a woman to lose her virginity outside marriage. In the context of the moral codes of large parts of Asian societies a woman is thereby considered to be 'damaged goods'.
[7]
[8]
[9]
No virgin - no bride? - crazy Asia [7]. - At the other hand there are youth magazines from Europe with emotions, sports, songs, music groups and analysis of sexuality [8,9].
Youth in Europe and North "America" is developing sexuality gradually during their youth reading much about it and developing a responsibility for it, mostly with first sex between 15 and 17. But Asian culture often blocks any youth development and also any development of sexuality. Asian mothers mostly educate their daughters saying that anything about sexuality would be "dirty" provoking fear blocking any sexual energy instead of learning to manage it. Also youth magazines do mostly NOT exist in Asia [8,9] where emotions, sports, songs, music groups and sexuality are the main topics - but in Asia all is taboo and forbidden for being "clean".
At the same time men in many Asian countries go to brothels and to brothel prisons from 13 years on learning using tortured, manipulated and extorted girls and women for their sexual needs, but just the same men want virgins for marriage. This kind of acting is schizophrenia. But also women are blocking men in Asia not knowing anything about sexuality and many Asian women often have vagina inflammation blocking any sex with men or husbands because they don't know how to handle their vagina well for a good sex life - and then women also send the men to the brothels and brothel prisons...
WOMEN Minister of Culture, of Education, and of Family in Asia are also forbidding anything about sexuality in Asia - but accept the brothels for men, where sex slavery is performed... The result is a sexual disaster with high AIDS rates and large groups of broken women stigmatized and without rights. Prostitution is mostly "illegal" in Asia - more schizophrenia is not possible. A disaster.
2.5: 'Tradition' of discrimination of pregnant and raped women in Asia
[Now follow examples of schizophrenic customs in Asia how Asian women are "handled" in certain situations]:
Indian logic: pregnant girlfriend sold to a brothel saving the status of the boyfriend's family
A thirty-year-old prostitute in a big brothel in Delhi's GB Road explained the disgrace that had brought her to sex work:
<I came from a large family and when I was thirteen I feel in love with a boy from my town. He promised that he would marry me so I started to have sex with him because I thought it was safe and that he would be my husband soon. Then I got pregnant. My boyfriend said we must run away and get married. So I ran away with him and he brought me to Delhi. Then he sold me to this brothel. I had to stay here. I was spoiled. My family wouldn't have accepted me and no man would marry me because I was pregnant. I've been in this place for seventeen years.>
[The boyfriend would loose hierarchical positions marrying a pregnant woman, and the family would also loose status against other families]:
The obsession with virginity is closely bound up with concepts of honor and position within male power hierarchies. A woman's conduct, her family's capacity to 'protect' her, and her ability to make a respectable marriage are important markers defining the status of families and the power of men. Crucially, this form of male competition is not so much about power over women as it is about power over other men.
Pakistani logic: honor killings in Pakistan killing women when there is only a suspicion of a relationship
In Pakistan, for instance, the izzat (honor) (p.36)
of men and their families has to be constantly reaffirmed - most significantly through their control of females. Generally, the higher the status of the family - whether it be in South, South-East or East Asia - the tighter are the controls that a family will impose upon its women. Logically, as the honor of families rests upon their women, higher status families have more to lose if their females transgress established codes. Most privileged women do not transgress these limits because they would not wish to jeopardise [endanger] their social and economic privileges, even if those privileges lead them to live circumscribed lives.
For some the costs of stepping outside the boundaries set by their families are awesome. In Pakistan, for instance, it is not uncommon for girls to be killed by their own brothers, cousins or fathers if they are suspected, even on the flimsiest and most ridiculous grounds, of having an illicit relationship. In a three-month period in 1996, sixty-six cases of karo kari (honor killings) were reported in the papers of Sindh province alone [12].
[12] Government of Pakistan: Report of the Commission of Inquiry for Women (Islamabad, August 1997), p.88
From the perspective of the murderous relatives these killings were honorable because they were interpreted as acts designed to preserve the reputation of the family.
[This really seems very strange: a family of a murderer has got a "good reputation"...]
Little monument in Germany against honor killing [10]
(Text: Murder is a crime and no matter of honor)
These honor killings in Islam world are also executed in many other Islamic states - but this has nothing to do with Quran but is a behavior with extremist law of Sharia. This is one of the taboo topics in Islamic world.
Asian logic: raped girls loosing virginity have to go to prostitution: Philippines, Bangladesh, Cambodia
The life stories of sex workers often have similar distinguishing marks. One of the common patterns, which was repeated in countries as far apart as the Philippines, Bangladesh and Cambodia, was rape as an entry ticket into prostitution. In societies in which there is little social interaction between men and women and little or no opportunity to form relationships outside marriage, virginity is highly valued as a symbol of inaccessible femininity. These are also societies in which there is a high demand for prostitution and in which the purchase of a girl's virginity and her 'freshness' carries a premium [13].
[13] Jean D'Cunha: The Legalization of Prostitution: A Sociological Inquiry into the Laws in Relation to Prostitution in India and the West (Bangalore: Wordmakers, 1991), p. 31-32
The other side of the coin is that once a girl has been deflowered she is then considered 'spoiled'. Even a victim of rape would be deemed a 'fallen' woman in these societies.
Supplement: Buddism and Catholic church are the same stupids with virgins
Buddha monument in a Buddhist temple in Phnom Penh, Cambodia [11]
Christian cathedral in Manila, Philippines [12]
It seems absolutely crazy: many Buddhist countries (like Cambodia) and Christian countries (like the Philippines) celebrate and torture the population with the same stupidity with virgins, and when girls are not virgins any more then they are downgraded for being prostitutes. Also in South "America" many "Christian" countries (Peru, Bolivia, Ecuador, Columbia) are celebrating virgin cults yet destroying any free development of their youths prohibiting any early love instead of educating sexuality well. Thus people are not prepared for adult life and become just crazy with alcohol and with a high criminality rate. Love is forbidden - but alcohol not. About drinking alcohol people know much in Asia - but about love they don't know hardly anything. And in many "Catholic" countries it's the same - with high murder rates...
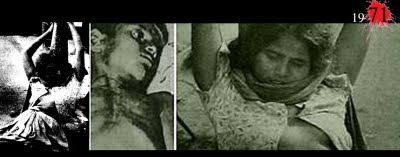
Logic in Bangladesh in the 1970s: Pakistani soldiers raped Bangladeshi women and girls downgrading them - families expelling the raped victims
An appalling example of this is the treatment meted out to victims of rape in Bangladesh. In the country's War of Liberation from Pakistan in (p.37)
the early 1970s Pakistani soldiers raped over 30,000 Bangladeshi women and girls [14].
[14]
-- Dina M. Siddiqi: 'Taslima Nasreen and Others: The Contest over Gender in Bangladesh'; In: Herbert L. Bodman and Heyereh Tohidi (eds): Women in Muslim Societies: Diversity Within Unity (Boulder, Colorado: Lynne Rienner, 1998), p. 208-209;
-- Santi Rosario in: Purity and Communal Boundaries: Women and Social Change in a Bangladeshi Village (Sydney: Allen and Uniwn, 1992), p. 104-105, quotes figures of 200,000 to 400,000 rapes.
Rape was used as an instrument of war. It was an attack upon the core of Bangladeshi society because the women were seen as the symbols of its honor and of the status of its men. After the war the women were called birangona and they were designated as war heroines in official discourse. But, in private, society marked them as impure. Whole families turned their backs upon their raped daughters, sisters, wives and mothers. There was no place for them at home because families could not bear the ignominy [bad event] and shame of an unchaste woman in their midst.
[And almost 30 years later girls and women in Bangladesh are going on to be downgraded yet - see this case]:
Supplement: Bangladesh war for independence from Pakistan in 1971 with mass rapes
Pakistani troops in Bangladesh on their flight in December 1971 [13]
Bangladesh, raped women by Pakistani soldiers 1971 [14]
Logic in Bangladesh in the 1990s: luring girl with a 'domestic job' - landlord raping the girl - landlady kicking the girl out of the house - lady in the street - a woman is selling the raped girl to a brothel
Almost thirty years later attitudes remain the same. Sex workers on the streets of Dhaka tell of how they were raped before becoming prostitutes. I met one of them, a woman in her early twenties who services her clients while standing by an open sewer. She explained that she had come to the city as a child.
<I don't know how old I was but my breasts had not begun to grow and I was very small. I came here because there was no one to care for me at home and a woman who knew my uncle said she could get me a domestic job. I got work in a nice house cleaning and helping to look after the little children. But after a while the master would not leave me alone. He raped me and when his wife found out I was beaten and thrown out of the house. What could I do then because I was broken? I had no place to live and no food. So I went with a lady to a brothel and she sold me there. I have been in the business ever since that time.>
Logic in 'Catholic' Philippines: lost virginity provoking often prostitution
Girls and women like this street prostitute have internalized the good woman-bad woman image. A very similar phenomenon can be found in the Philippines, despite its higher levels of economic development. Legitimate sexuality, at least for women, is found only within marriage. The 'home, hearth and heaven' myth is very strong (p.38)
in Filipino Catholicism and so is the cult of virginity. A girl who is raped, or who has a pre-marital relationship that turns sour, will frequently be burdened with the shame of no longer being a virgin. For some of these girls it is a shame that leaves them no options other than to become a prostitute because they honestly believe that they are no longer worthy enough to become the wife of a decent man.
Logic in Asia: raped women are not worth a marriage - raper can become the pimp
In the most sexually and gender-repressive societies in Asia rape is an initiation into prostitution. A raped girl is unable to marry because she is no longer a virgin. Such women resort [go to] to sex work because it is the only form of work available to them and because they cannot survive as single women. Ironically the trauma of the rape and the devastating consequences that flow from it can sometimes bind the girl to her rapist. The perpetrator of the crime then becomes her trafficker and her pimp [15].
[15] Bangladesh National Women Lawyers' Association: Survey in the Area of Child and Woman Trafficking (Dhaka, 1997), p. 36-37
In other words he creates the prostitute and then he profits from her.
Logic in Asia: hindering a rape by prohibiting contact between women and men - child marriage as a prevention of a rape - rape law driving more and more girls into prostitution business
There is a horrible kind of circular logic in the attitudes to women in those societies that are the most repressive. Women have to be guarded from predatory males, or they have to be secluded [isolated] so that the power of their sexuality does not tempt men. In Bangladesh this is sometimes cited as a justification for child marriage [16].
[16] Bangladesh National Women Lawyers' Association: Survey in the Area of Child and Woman Trafficking, p.33
It is portrayed as a kind of preventative measure against child abuse on the grounds that a young unmarried girl, by the simple fact of her existence, is a sufficient reason to incite a man to rape. Women are kept in their place by fear. If they try to step out of traditional roles they are considered fair game. Yet at the same time, while they remain in their traditional spheres, the system that oppresses them continues to be validated and confirmed.
All of the world's major religions and ideologies discriminate against women - in practice if not always in theory. Asia's principal religious traditions reflect and perpetuate gender discrimination. In doing so they help to perpetuate institutions such as prostitution even if most do not explicitly encourage the sale of sex. In some instances, however, they actually encourage prostitution (p.39).
2.6: More Asian discrimination against women with 'bad karma' in Theravada Buddhism - devadasi temple system
Logic of Theravada Buddhism in racist Thailand and Burma: women have a 'bad karma' - women have to serve much also making prostitution for being a man 'in her next life'
Buddhist texts would have you believe that women are just as capable as men are of achieving spiritual perfection. Unfortunately, social practice does not marry with this gender-sensitive viewpoint and women are seen as less spiritually refined because they are attached to the very unspiritual, material world by their basic reproductive functions. A woman is thought to have been born as a woman because of bad karma. In order to overcome this disadvantage a woman has to make more religious merit than men. According to the Theravada Buddhist tradition of Thailand and Burma, a son may make merit by becoming a monk for a few months. But for a daughter there is no similar option. Instead she is encouraged to make merit by caring for their parents. If she does this well, and earns money for her family, she can, conceivably, be reborn as a man in her next life. This desire to help their families has been identified as a powerful factor pushing young women into prostitution in Thailand [17].
[17] Marjorie Muecke: 'Mother Sold Food, Daughter Sells Her Body: The Cultural Continuity of Prostitution'; Social Science and Medicine, vol. 35, 1992, p. 891-896
Buddha hill in Pattaya, Thailand [14]. Looking good? But this Theravada Buddha system is instructing that women have to serve for being a boy in their "next life". Crazy! Ting tong!
According to Wikipedia Theravada Buddhist tradition is spread within Sri Lanka by 80%, in Burma by 89%, in Thailand by 94%, in Laos by 60%, in Cambodia by 95% [web03]. Theravada Buddhism and reincarnation belief in being a minor girl becoming a superior boy in the next life provoke that girls want to serve their family making money by prostitution - because the government is not installing good jobs in the countryside. Crazy logic. Human rights, good jobs in the countryside and social networks and simple contraceptions which are easy to handle would really be better...
Hinduism prescribing women as dangerous and men have to manage her positive and negative energies
Hinduism stresses the importance of women's purity and chastity. A woman is thought to have a dual nature: there is the divine, nurturing and creative aspect of femaleness, and there is her dangerous, evil and carnal side. A man is essential in order to control and subdue her. Only a man can harness the positive aspects of her nature and repress the negative. Women are therefore simultaneously devalued and worshiped. They are caring, devoted and maternal or they are destructive, anarchic and intensely sexual beings. They are wives and mothers or they are voracious whores.
Hinduism with religious "devadasi" prostitution in a garb (English colonialism destroyed the support for religious dancers): girl marrying a god and dedicated to a temple and making it's living with prostitution, or manual labor or agriculture
It is not a paradox but an inevitability that Hinduism makes provision for institutionalized prostitution. This form of prostitution is dressed up in religious garb in order to give it a gloss of respectability. The South Indian devadasi system is the best example of this [18].
[18]

Devadasi dancer with a Melattur style [16].
In former times before English colonialism these temple dancers got everything by public support.
Since English colonialism destroyed the support system the dancers have to make money with prostitution, manual labor or agriculture.
-- Joint Women's Program: Banhi: Prostitution with Religious Sanction. The Devadasi Problem, Venkatasani / Jogini and the Basavi Cult. Third edition (Delhi 1988).
-- I am also indebted to Prighi Patak of Prerana, Mumbai, for her detailed explanation of the devadasi system and its impact upon prostitution in Kamatipura.
Even though it is technically illegal, the practice of dedicating prepubescent girls to a deity continues today. This is how the system works: a rich patron buys a girl from an impoverished family and then oversees [controls] her marriage to a god and her dedication to a temple (p.40).
He does this in the alleged hope of amassing religious points for himself and his family. From then on the girl is prohibited from marrying and, when she approaches puberty, her virginity is auctioned off to the highest bidder - usually a leading local figure and sometimes, unsurprisingly, the very patron who dedicated her to the temple in the first place. As the devadasi cannot marry and seek the comfort and economic security of a family. She is tied to a life of religious prostitution. And, in turn, her daughters will follow in her footsteps by becoming devadasis themselves.
[Supplement: temple dancers making their living with prostitution, manual labor or agriculture
The existence being a dancer in the temple and prostitute for everyone developed because during English colonial times the status of the temple dancer was outlawed and since then there is no religious support of the religious woman dancer any more. And many dancers are making their living also with other businesses: <A study from 1990 recorded that 45.9% of devadasis in one particular district were prostitutes, while most of the others relied on manual labor and agriculture for their income.> [web01]
Hinduism: Badis in Western Nepal, a prostitute caste: first entertainers were offering shows and sex - now girls are prostitutes and sons are pimps
Nepali Badi woman Soni Badi, forced prostitute without rights [17]
<Mura, Far Western Province, Nepal, Nov 2007. The Badi caste in Nepal is a Dalit 'sub-caste'. Many Badi women are forced into prostitution and end up being trafficked to Mumbai's sex industry. Soni Badi, 25, is a sex worker. As a Badi Dalit she is prevented from owning land, has little access to education and other services crucial to sustain life and avoid lifelong poverty.> [web05]
The Hindu caste system incorporated prostitute castes. In Western Nepal the Badis are an untouchable caste of around 7,000 people [19].
[19] Thomas Cox: The Badi: Prostitution as a Social Norm Among an Untouchable Caste of West Nepal (unpublished manuscript, undated).
Traditionally they were entertainers who offered their patrons cultural shows as well as sex. Now their functions are more basic. The daughters follow their mothers to become sex workers and the sons become pimps. In this caste the traditional South Asian lament at the birth of a daughter and the celebration at the birth of a son is reversed. A pretty daughter is no longer a liability - by selling sex she has become an asset. At one time this reversing of accepted attitudes applied only to small sections of Asia's poor but today it is changing. Increased poverty, higher material expectations, and greater knowledge of economic opportunities mean that whole impoverished communities in less-developed Asia see their girls as a way to survive and sometimes simply as a way to comfortable living.
Perverse logic in 'Catholic' Philippines: sex is 'sin' for women - only within marriage sex is not a 'sin' - the less she knows about sex the 'better' she is
Christianity did not make much headway [provoke progress] in Asia. But where it proselytized well - like in the Philippines - it did so with great zeal ["good work" destroying other cultures]. The Philippines has all the repressive qualities of traditional Catholicism mixed with a good measure of Asia's group mentality. The mixture is a very troubled one for Filipina women [20].
[20] I am indebted for these insights to discussions with Emma Porio of Ateneo de Manila University and Amparita S. Sta. Maria of the Ateneo Human Rights Center, Manila.
Sex is equated with sin, at least for women, and the only legitimate form of female sexuality must be found within the bonds of marriage. A girl's reputation in the Philippines depends upon her ignorance of sex and her sexual behavior (which should be non-existent). She (p.41)
should not even ask about the subject in case she should be suspected of having impure thoughts. Even knowing about AIDS and how it is transmitted may pose a risk to her social standing.
2.7: Facade and reality about sex life in Asian societies
Islam: Qur'an says men and women are a 'complementarity' with equality of men and women - but in reality Muslim societies let men lead
When Quran [18] would be the only book as a guideline for Muslims, Islam would be absolutely peaceful
In this Shariah there is a tolerant marriage code, but only tolerant for men. When the man is a good one, it can be lucky with the woman or with women. But when women have a "wild" relation, then they can get hard punishment for it up to death penalty, depending on the men.
Rape is disastrous for women in Sharia Islam, not for men.
Stealing can be punished hard and many men remain with only one hand. Beating women to the contrary is tolerated what seems not to be understandable today.
Psychology, prevention and social work as means against criminality do not exist (yet) in this Islamic law otherwise it had been reformed already.
It would be easy to reform it, but this would mean to copy parts of systems of European countries which were Colonialists in the 19th century.
But Islamic propagandists don't like European elements so much. That's why the psychological development in Islam is blocked and Islamic groups even try to "colonize" Europe as a revenge for Colonialism and mass robbery which was performed in 19th and 20th century. And Europe and "U.S.A." are supporting Arabia with it's harsh Shariah law by oil business...
Apologists for Islam's abysmal treatment of women point to the fact that Islam does not hold women to be ideologically or biologically inferior to men. The spirit of the Qur'an speaks of the complementarity of the sexes and the ultimate equality of men and women. Tragically this is not the way many Muslim women must experience their relationships with men.
Muslim societies take it as axiomatic that men are the dominant and superior sex. Societies are structures to express this, so men in countries like Bangladesh and Pakistan marry women who are significantly younger than they are, and who are frequently little more than adolescents. Men justify this by their superiority but, in fact, it also creates that superiority too by generating relationships that have wildly unbalanced power dynamics [21].
[21] Arno Schmitt and Jehoeda Sofer (eds): Sexuality and Eroticism Among Males in Muslim Societies (New York: Haworth Press, 1992), p.3
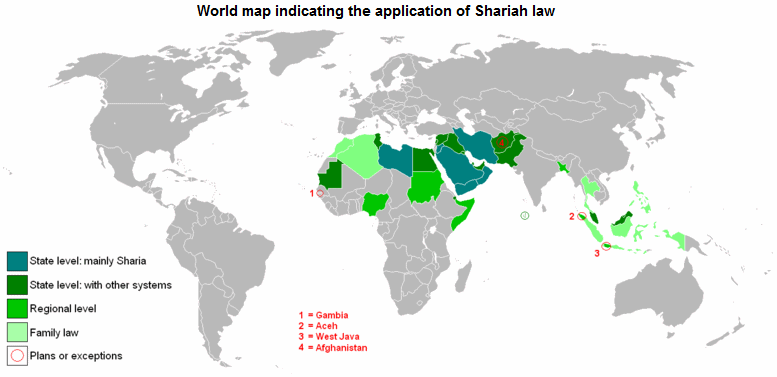
World map indicating Shariah law / Shariah rule [20]
Islam societies define women as destructive
Islam sees women as destructive. Females are suffused with fitna - inordinate sexual powers that have to be contained so that they do not disturb the harmony of society and lead to chaos. Men have to be protected from this sexual power so that they are not provoked and drawn away from a righteous path. Men, in this sense, are always seen as the victims of female sexuality [22].
[22] Afiya Shehrbano Zia: Sex Crime in the Islamic Context: Rape, Class and Gender in Pakistan (Lahore: ASR Publications, 1994), p.15
In the words of one of the leading feminist scholars on the Muslim world, 'the whole Muslim social structure can be seen as an attack on, and a defense against, the disruptive power of female sexuality." [23]
[23] Fatima Mernissi: Beyond the Veil: Male-Female Dynamics in a Modern Muslim Society (New York: John Wiley, 1975), p.14
Remedies are found in the monitoring of women and in the separation of the sexes. The rich place their women in seclusion (purdah) when they become nubile [ready for marriage after their menarche]. Others who are conservative, but unable to afford the luxury of purdah, are veiled whenever they leave the confines of the home.
Confucianism in China, Korea and Japan with 'order, harmony and hierarchy' as a facade
China, Korea and Japan share a common Confucian heritage that is built around the concepts of order, harmony and hierarchy. In pre-modern East Asia individuals had a specific place within this hierarchy: children were obedient and showed respect to their (p.42)
parents; the people owed allegiance to the emperor; and women showed deference to their husbands. To have questioned these articles of faith would have been to challenge the entire social system.
China: rich men with many wives and concubines - sold children from poor families e.g. in Thailand and Nepal - sold daughter sending money home
Viewing women as a commodity has a long pedigree [tradition] in China. Rich men had many wives and concubines, and daughters were seen as property of the family: they were possessions to be disposed of as their father wished. In contrast, sons were important. They belonged to the family of their birth and it was only through the male line that a family's descent could be traced. Women were peripheral [not important]. Their bodies were simply the vehicle by which the patriarchal family perpetuated itself.
Pagoda temple in Changshu, China. Architecture is perfect, but arranging of social problems not at all...
Children - especially girls - from poor families were sold as domestic servants when times were hard [24].
[24] For fascinating analysis of this, see
-- Maria Jaschok and Suzanne Miers (eds): Women and Chinese Patriarchy: Submission, Servitude and Escape (London: Zed Press, 1994), and
-- Maria Jaschok: Concubines and Bondservants: The Social History of a Chinese Custom (London: Zed Press, 1988)
The pretty girls became prostitutes. When harvests failed and famine threatened, the market was flooded with children from desperate families and the going rate for a child would plummet [come down]. By the early twentieth century the selling of daughters had changed subtlely. They were not usually sold outright but were pawned and parents or guardians received a 'loan' upon which the girl acted as collateral [25].
[25] Gail Hershatter: Dangerous Pleasures: Prostitution and Modernity in Twentieth-Century Shanghai (Berkeley: University of California Press, 1997), p. 196-197
This system operates in large parts of Asia today when families in Thailand and Nepal, for instance, take an 'advance on their daughters' earnings in the sex trade.
China 1950: communist laws for women's rights and elimination of polygamy - and all reappeared in the 1970s in poor provinces: women migrating from poor to rich provinces - woman trafficking from abroad to the poor provinces
In 1950 the newly victorious Chinese Communist Party enacted the Marriage Law. This law removed abuses like polygamy, concubinage and forced marriage. At least it did on paper. The Chinese state clamped down on prostitution. But in reality these evils were never fully eradicated and the old practices made a public comeback in the 1970s. In particular, trafficking in women reappeared in poor and remote mountain provinces. Many women from these regions had migrated and had married men in richer provinces in an attempt to build a better life. Unfortunately, the men left back at home were obliged by tradition to remain with their parents and to continue the family line in the family farm. However perpetuation (p.43)
of the bloodline was proving difficult in the absence of women to marry and mate with. The women who remained could command a hefty bride price as a result of their scarcity and few families were willing to foot [pay] such a substantial bill. An answer to the problems of these eager bridegrooms was found in the marketplace. A supply of brides was brokered by traffickers who delivered a wife for a quarter of the amount necessary for bride price.
Some of these brides were from even poorer communities and they were willing to be married to an unknown man in the hope that he would provide them with improved economic security. Many, however, were tricked [resp. they were lured with promises for good jobs] and forced into the match.
The phenomenon of the purchased wife is common in the remoter regions of China. Buying a wife is not considered to be a reprehensible practice in these communities because it builds on customary behavior. Matchmakers and go-betweens were familiar characters in the arranged marriages of traditional China. Today's traffickers and sellers of women have a socially legitimate ancestry and those who buy their women do not believe that they are doing anything wrong in using the services of an agent specializing in human beings [26].
[26] Xia Peijun: Country Report on China. Paper presented at the Regional Meeting of the Coalition Against trafficking in Women. Dhaka, Bangladesh, June 1998
Sexual access to females is both a privilege of male power and a symbol of that power. So rulers and local elites in Asian societies, as elsewhere, displayed and enjoyed their power by possessing and controlling women's bodies. A few had harems, many had multiple wives, a lot had concubines and most helped themselves to the local village girls and poor urban women. Things have not changed much.
[Addition: Life in a harem - how was it?
The author Louise Brown never mentions how life for these women in China was with rich rulers, how the conditions were, if they were helped in learning or how was their function within the household. Without these indications life of women with a rich ruler group cannot be rated].
| Share: |
Facebook |
|
Twitter
|
Sources
[web01] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Devadasi
[web02] Claire Ellis: Culture Shock! Vietnam. A Guide to Customs and Etiquette; Times Books International, Singapore, p.60
[web03] http://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Theravada
[web04] http://nexttunes.blogspot.com/2012/12/the-largest-genocide-during-bangladesh.html
[web05] http://idsn.org/caste-discrimination/key-issues/forced-prostitution/
Photo sources
[1] hormone ring "Nuva Ring": http://www.intimatemedicine.de/gesundheit-und-sexualitaet/verhuetung-mit-vaginalring/
[2] poverty in Chiang Mai, northern Thailand: http://wordsofeternallife.org/tag/poverty/
[3] map of Thailand: http://www.macach.com/reise/th/d_thailand.php
[4] China, relation between men and women 1980-2020, graphics: edition.cnn.com/2012/11/14/opinion/china-challenges-one-child-brooks
[5] Thai mother from Paudung minority nursing baby: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=J9pT7MflqQw
[6] help for widows by Aim Asia network: http://aimasia.in/mercyprojects.php?n=10
[7] no virgin no bride: http://www.asianpussylover.com/2011/02/
[8] youth magazine Bravo 2011: http://www.relativ-kritisch.net/blog/allgemein/japan-das-nukleare-beben
[9] youth magazine Bravo Girl 2011: http://www.zeitschriften-cover.de/bravo-girl-cover-oktober-2011-x5764.html
[10] little monument against honor killings:
http://www.igfm.de/themen/scharia-islamisches-recht-und-menschenrechte/frauen-und-scharia/ehrenmorde-in-deutschland-bka-studie-2006/
[11] Buddha monument in a Buddhist temple in Phnom Penh: http://wellisphotography.photoshelter.com/image/I0000rv3K6FW1DCM
[12] Christian cathedral in Manila: http://members.virtualtourist.com/m/p/m/1d2d34/
[13] Pakistani troops on their flight in December 1971: http://einestages.spiegel.de/external/ShowTopicAlbumBackground/a22281/l9/l0/F.html
[14] raped women in Bangladesh by Pakistani soldiers 1971: http://nexttunes.blogspot.com/2012/12/the-largest-genocide-during-bangladesh.html
[15] Buddha hill in Pattaya, Thailand: photo by Michael Palomino 2012
[16] Devadasi dancer with Melattur style: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Melattur_style
[17] Nepali Badi woman Soni Badi, forced prostitute without rights: http://idsn.org/caste-discrimination/key-issues/forced-prostitution/
[18] Quran: http://www.andrewbostom.org/blog/2010/06/28/post-modern-coin-age-of-a-failed-policy%E2%80%94mcchrystal-tocqueville-and-the-koran/
[19] Shariah law: http://asqfish.wordpress.com/2010/09/19/what-is-the-term-sharia/
[20] world map indicating Shariah law: http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Countries_with_Sharia_rule.png
[21] Chinese pagoda temple in China in Changshu:
http://view.stern.de/de/picture/China-Tempel-Chinesischer-Changshu-Tempel-Changshu-Grau-2189284.html
^