2.8: Women trafficking for
prostitution for an 'open market'
Women trafficking in Nepal to Kathmandu -
concubines in feudal Indonesia
|

The old center of
Kathmandu [22]
|
|
In nineteenth-century Nepal thousands of girls from hill
tribes in the Himalayas were taken to Kathmandu [the
capital of Nepal] to become sexual partners of men from
the ruling Rana family. In feudal Indonesia the king's
power was measured, in large part, by the number of
concubines he kept at court [27].
[27] Lin Lean Lim (ed): The Sex Sector: The
Economic and Social Bases of Prostitution in Southeast
Asia (Geneva: International Labor Organization, 1998),
p.29
Women were a commodity and a kind of currency.
This provided a firm and extensive foundation for the
modern-day commercialized sex industry. Capitalism has
added its own inequities and injustices to traditional
aspects of gender exploitation so that customary forms of
subservience and exploitation have been repackaged. If
anything this has served only to entrench traditional
structures of privilege.
[Again
the author never mentions how life for these concubines in
Indonesia was, no conditions are prescribed, no learning,
no function in the house. The book seems to be very
incomplete].
|

|
|
New
York stock exchange [23]: the more
globalization we have - the more poverty we
have - the more prostitution is in the
world. And poverty rates are not indicated
in the balance of the stock exchange... |
Globalization with more poor population provokes more
girls for prostitution
The inescapable forces of globalization and economic
liberalization have pushed more and more poor girls into
prostitution throughout the world. The unrestrained
capitalism that is emerging in large parts of Asia makes
no allowances for the vulnerable and for the dispossessed.
In that sense it harmonizes perfectly with traditional
Asia's hierarchical contempt for the lower orders.
Capitalism's rawest and most rapacious forms - including
the sex industry - seek to profit from that vulnerability.
Woman trafficking from Vietnam to Cambodia
In Vietnam, to take one example, there has been an
increase in trafficking and prostitution. In part this can
be explained by the re-emergence of traditional attitudes
to women, as the ideals of the Vietnamese revolution have
atrophied [reduced] under the twin pressures of a failing
command economy and the reach of global capitalism.
Intimately associated with this, and fundamental to the
re-emergence of large-scale prostitution, are the growing
disparities between the rich and the poor and the
disintegration of the structure of the family under the
impact of economic liberalization [28].
[28] Annuska Derks: Trafficking of Vietnamese Women and
Children to Cambodia (Geneva: International Organization
for Migration, 1998), p.9
[When Vietnamese are trafficked to Cambodia this
concerns for example girls and young women from poor Mekong
Delta lured and tricked to Phnom Penh brothel districts.
Vietnamese women are also trafficked to China where is a
lack of women by the Chinese 1 child policy and the
preference for sons. But not only China is the aim for
Vietnamese for getting foreign currency. See here the
general indication of www.humantrafficking.org of 2011:
<Vietnamese men, women, and girls are trafficked for
sexual and labor exploitation in Taiwan, Malaysia, South
Korea, Laos, the United Arab Emirates, Japan, China,
Thailand, Saudi Arabia, Libya, Indonesia, the United
Kingdom, the Czech Republic, Cyprus, Sweden, Trinidad and
Tobago, Costa Rica, Russia, and elsewhere in the Middle
East. In both sex trafficking and labor trafficking, debt
bondage, confiscation of identity and travel documents, and
threats of deportation are commonly utilized to intimidate
victims.> [web01]
|
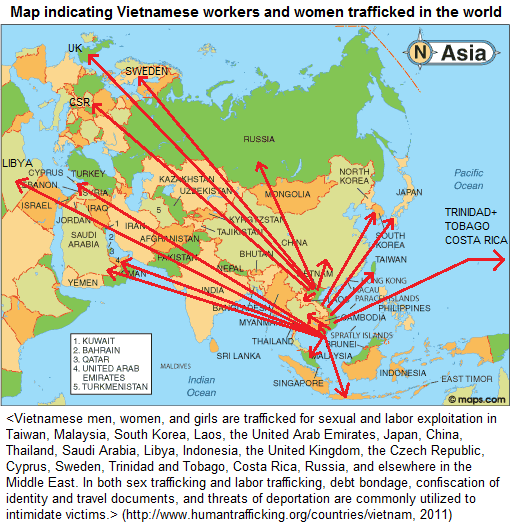 |
Map indicating
Vietnamese workers and women trafficked in the
world (2011) [24]
The basic map is from www.maps.com
The indications of a web site about human
trafficking with Vietnamese people in 2011
reports:
<Vietnamese men, women, and girls are
trafficked for sexual and labor exploitation in
Taiwan, Malaysia, South Korea, Laos, the United
Arab Emirates, Japan, China, Thailand, Saudi
Arabia, Libya, Indonesia, the United Kingdom, The
Czech Republic, Cyprus, Sweden, Trinidad and
Tobago, Costa Rica, Russia, and elsewhere in the
Middle East. In both sex trafficking and labor
trafficking, debt bondage, confiscation of
identity and travel documents, and threats of
deportation are commonly utilized to intimidate
victims.>
(http://www.humantrafficking.org/countries/vietnam)
|
|
|
|
According to news of September 2012 young Vietnamese women
were lured to China for marriage but in many cases they
suffer beatings or are even sold into prostitution and
Vietnamese families are pleading for helping them [web02].
Woman trafficking in Cambodia - 'on the open market'
A similar trend can be seen in Cambodia, where the
institution of a free market economy in the early 1990s
led not only to the enjoyment of pleasant economic
freedoms but also to the freedom to trade girls on the
open market. Today there is nothing in Cambodia
that you cannot buy.
2.9:
Reasons for prostitution: poor, minorities, castes,
and rapes
General indication: girls for prostitution are mostly
from the poor, from minorities and low castes, often
illiterate
The bulk [the big mass] of prostituted women in Asia come
from poor communities, tribal groups, low castes and
ethnic minorities. Their origins are almost as despised
[downgraded] as their occupation [prostitution]. In the
less developed parts of the region most sex workers
were born and raised in poor rural areas. Two thirds of
the girls and women who enter prostitution in India come
from areas that are drought prone [29].
[29] National Commission for Women: The Velvet Blouse (New
Delhi: Government of India, 1997), p.9
Throughout the whole of less-developed Asia the majority
of girls (p.45)
who sell sex are poor and often illiterate and the sex
industry likes them because their youth and lack of
education makes them easy to manipulate and control.
Thailand: Japanese
customers looking for young AIDS-free Thai girls
They also possess another important selling point: because
they come from remote regions, and because they are young,
clients are reassured that they are free of sexually
transmitted diseases and HIV. Some customers, particularly
Japanese men, are so insistent about this disease-free
requirement that they visit villages in Thailand purely to
buy sex with a girl who is guaranteed to be fresh and safe
as well as cheap [30].
[30] Siriporn Skrobanek: Traffic in Women: Human Realities
of the International Sex Trade (London: Zed Books, 1997),
p.34
[Addition: North
of Thailand: poverty is installed there deliberately -
police officers are the brothel owners
The government in Bangkok is not interested in an
economic development of the countryside therefore
poverty in the countryside is especially high. And in
northern Thailand especially the local police officers
are the brothel owners themselves selling virgins then
who are eventually two times operated already...]
India: prostitutes 'dalit' castes
(untouchable) and from tribal groups
|

|
|
Dalit women
in India with water [25].
6 villages have not one single well. This is
really a discrimination - and selling 10 years
old children to temples is a reality, and
prostitution is often a forced occupation...
|
In India the vast majority of prostituted women are from dalit
- or untouchable - castes and also from the tribal groups
[31].
[31] National Commission for Women: Societal Violence on
Women and Children in Prostitution (New Delhi: Government
of India, 1996), p.12
[From Dalit people come the girls sold to temples
for being a Devadasi dancers, and in many cases these
dancers end like prostitutes in the big towns of India in
the brothels [web03] And AIDS is a big problem for them when
they chose to be prostitutes [web04]
These women suffer a triple burden of
exploitation: they are poor, they are untouchable and they
are female. For some, the intersection of these dreadful
disadvantages can be devastating.
Girl raped in a Bengali village - no money for a dowry
- and brought to a brothel - and as a prostitute she
cannot go anywhere
|
|
|
Map
with India, Bengal, and Bangladesh [26],
with Calcutta, Mumbai, and Dhaka

Village
of West Bengal [27],
gangs are governing performing rapes,
justice is nowhere and the victim has to
go...
|
I met a young
prostitute in a Calcutta brothel who was from an
untouchable caste. She looked about fifteen but she
claimed that she was nineteen. She was a wretched, thin
child wearing an ill-fitting Western-style dress and she
carried the look of someone who had been beaten by life.
This is her story:
<I am from a village a long way from here in
West Bengal. My family is very, very poor. There were four
children in our family. My father is dead and my mother
could not feed me and my brothers and sister. We did not
have a proper house and we were always hungry. Everyone in
our village looked down on us because we are poor and from
a low caste.
When I was thirteen some youths from our village took me
into a field away from the village and they raped me.
There were five of them and they were from high-caste
families. I was crying and I went back to the village but
the youths said I went with them willingly. The village panchayat
(council) said that I had a bad character and was not
(p.46)
respectable and that I shouldn't tell lies about the
youths. They told my mother that I had to leave the
village because I was a bad influence. But no one wanted
to marry me and my mother could not afford a dowry so she
brought me here. There was nowhere else I could go.
Sometimes I can send my mother a little money and this
makes her happy. It helps to buy food for my brothers and
sister. I can't go back to my village because they think
that I'm bad and they know what work I do. This place is
my home because I have nowhere else to go to. I'll go on
working here for as long as the clients want me.>
2.10: Women trafficking in Nepal - women's
migration in and to Thailand
|

|
|
Suspension
bridge in Nepal [28]
|
Women trafficking
from Nepal to India: girls in prostitution - mostly
from marginalized hill tribes - poverty of mountain
dwellers
In Nepal increasing poverty [estate 2000] is
pushing women from a wide range of castes, including
high-caste women, into selling sex [32].
[32] UNICEF: A Situation Analysis of Sex Work and
Trafficking in Nepal With Reference to Children
(Kathmandu, June 1998), p. 19-20, 36
But the majority of prostitutes are from the politically
marginalized hill tribes, and almost all of the
girls trafficked to fill north Indian brothels are from Tamang,
Lama, Magar and Gurung ethnic minorities [33].
[33] UNICEF: A Situation
Analysis of Sex Work and Trafficking in Nepal With
Reference to Children (Kathmandu, June 1998), p.51,56
Supplement:
Nepali ethnic groups with some hill tribes
|
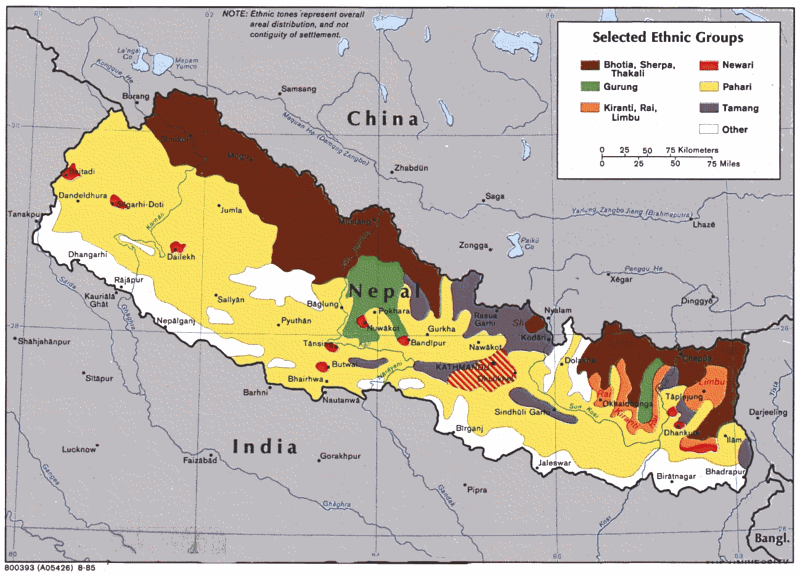 |
Map of Nepal indicating some ethnic groups: Bhotia,
Sherpa, Thakali, Gurung, Kiranti, Rai, Limbu,
Newari, Pahari, and Tamang [29]
-- brown: Bhotia, Sherpa, Thakali
-- green: Gurung
-- orange: Kiranti, Rai, Limbu
-- red: Newari
-- yellow: Pahari
-- violet: Tamang (also called "Murmi" or "Bhotiya"
[web05]
-- white: other
|
The mountains of Nepal are a
paradise for trecking and hill climbing tourists.
Unfortunately also criminal human traffickers are
coming there visiting these poor villages for
"recruiting" staff for brothels in the big towns
of India. The girls and young women are simply
lured with a job "in the city". See the photos of
the hill tribes of Tamang, Gurung and Magar. Since
2006 there is a kind of democracy in Nepal. If
something is changing can be seen on the latest
web sites in the Internet.
 [30] [30]  [31] [31]  [32] [32]  [33] [33]
Nepal, Tamang hill tribe girls [30], Tamang chief
with drum [31], Gurung hill tribe women [32], Gurung
typical dresses [33]
 [37] [37]  [38] [38]  [39] [39]
Tamang village in Nepal [37], Gurung village
of Dhampus in Nepal [38], Gurung village in Nepal
with original agriculture on a rice field [39]
|
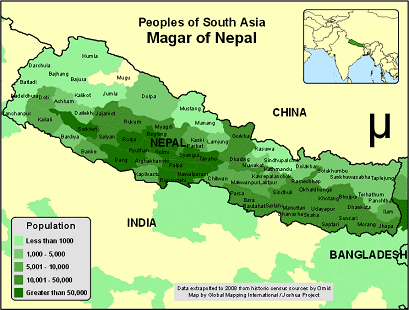 [34] [34]  [35] [35]  [36] [36]
Map of Magar ethnic group in Nepal [34], Nepal,
Magar ethnic group, women in traditional dress [35],
Nepal, Magar ethnic group with Kauda dance [36]
 [40] [40]  [41] [41]
Nepal, Magar stone architecture, photo by Nick Mayo
[40], Nepal, Magar village of Upallo Sera [41]
|
Their other distinguishing
characteristic is that half of these girls come from
families that are considered poorer than other families
in their own communities [34].
[34] UNICEF: A Situation
Analysis of Sex Work and Trafficking in Nepal With
Reference to Children (Kathmandu, June 1998), p.59
As most Nepali households are grindingly poor, this is
poor indeed.
Nepali's beauty hides desperate poverty. Tourists trek
along scenic Himalayan trails taking photographs of
charming villages, engaging children and breathtaking
mountains. It is easy to see lots of smiles but so much
harder to see the poverty that leaves 50% of children with
stunting as a result of malnutrition [35].
[35] UNICEF: Children and Women of Nepal: A Situation
Analysis 1992 (Kathmandu: UNICEF, National Planning
Commission, Government of Nepal, 1992), p.64
According to the World Bank around 40% of people live in
absolute poverty. In other words, their income will not
provide them with enough food to meet minimum calorie
requirements. Development has left many Nepalis far behind
[respectively corrupt and racist government is not doing
anything with the mountain dwellers. In 2006 monarchy was
eliminated and a kind of democracy was installed]. A
glance at national per capita income suggests that the
average Nepali is better off now [estate 2000] than thirty
years ago. Many of the poor would dispute this, and
anecdotal evidence indicates that the poor are getting
poorer. Certainly the gulf between the 'haves' and (p.47)
the 'have nots' is increasing year by year. Girls from
communities like these staff large numbers of India's
brothels and the sex industry has grown fat upon the sale
of their flesh.
Thailand: racist and corrupt government against
populations in the north and in the north-east - hard
work in the sun - cash economy provoking a breakdown in
Thai farming
The disadvantaged north and north-east of Thailand are
traditional recruiting grounds for the sex industry. These
areas of Thailand are poor compared with the more
prosperous central and southern regions. They are areas in
which the traditional rural economy has been weakened by
decades of maldevelopment. As in most Asian countries a
chasm has opened up between the urban areas, which have
grown richer, and the rural areas, which have stagnated
or, in some cases, declined [because racist and corrupt government
is against rural population and almost all industry is
only installed in Bangkok]. The sex industry has
been a principal beneficiary of this division.
 [42]
[42] 
[43]

[44]
Northern Thailand,
a village of the Akha [42] - Northern Thailand,
sisters in the village of Akha [43] - northern Thailand,
agriculture [44]
[People in agriculture is often protecting themselves from
the sun because they don't want a brown skin but a white
skin like the Thais in the towns...]
Supplement:
racism in Thailand against rural population:
hardly industries in the countryside - and
north and north east of Thailand are
deliberately flooded for "protecting" Bangkok"
Racist government in Bangkok is generally
against the rural population and almost all
industries are only concentrated in Bangkok.
Additionally during the rainy season the east
and north east of Thailand are deliberately
flooded for sinking Bangkok is not going down
now already. Thus there is a channel system
provoking that east and northeast of Thailand
are staying deliberately under water during at
least 3 to 5 months protecting Bangkok from the
floods of monsoon. Therefore in big regions in
the east and north east of Thailand any economy
is completely in a standstill during 3 to 5
months and therefore nobody is investing there.
And thus this is one of the breeding regions for
girls going to prostitution business then. It
seems strange that writer Mrs. Louise Brown does
not mention these important connections with
racism against rural population in Thailand and
with the deliberately provoked floods, partly
several meters high and during months during the
rainy season. As a tourist one can see this
perverse flooding system in Thailand in any
online newspaper...
 
Floods in Thailand in Prachinburi province, Sep
24, 2013 [x002] - Floods in the
town of Kabinburi in Prachinburi province, mother
and child, September 28, 2013 [x003]
 
Flooded Buddha temple, news
from Oct 3, 2013 [x004] - Chachoengsao village
in the east of Bangkok meters high under
water, one man died by drowning, news from Oct
14, 2013 [x005]
And now one must not
imagine that the Thai government would do
something about it with dams, dikes,
technical relief organization or such stuff.
NO! There is nothing done and in this way
poverty and the prostitutes are
systematically created and produced in those
regions! This poverty in the countryside and
this destructivity is a part of the perverse
male and racist Thai system and women are
not fighting for their rights of protection
everywhere - but at the end all are just
drinking whiskey and from 2020 on Bangkok is
sinking under 0 meters officially and nobody
knows what will happen then...
|
In Thailand, the rural
sector has been badly neglected. Just like in Nepal,
scenic villages and traditional houses are charming to
look at but they are horrible to live in [there is mobile
phone, but there mostly no Internet until today (2013).
Humans there are mostly living without tables and without
chairs yet. All life is on the floor. Parents don't know
what is "homework" and books do not exist. Often there is
no water tower either and therefore there is no running
shower etc., but beer and whisky is always running. Thus
all money which could improve the living standard there is
given out for beer and whiskey, in the east of Thailand
also for vodka. And the alcoholic party begins at 10
o'clock in the morning already. I saw it with my own
eyes... (2013)].
Pretty girls working in the fields look quaint and
colorful on postcards, but a day's backbreaking labor
in the sun is barely sufficient to provide them with
basic subsistence. Around thirty years ago the
introduction of a cash economy into the country's
rice belt led to a breakdown in Thai farming. It made
scratching a living from the earth in the poorer parts of
the country even harder. Young people from the countryside
have been leaving for the cities ever since. Some have
gone to work in factories and in the service sector. Many
of the girls are sent to provide sexual services to both
Thai and foreign men. And the provision of these services,
like the services provided by girls from Nepal, helps to
prop up [support] otherwise economically unsustainable
family farms.
Thai brothel keepers seeking for Thai girls from the
mountain tribes - measures by Thai government and NGOs
|
|
|
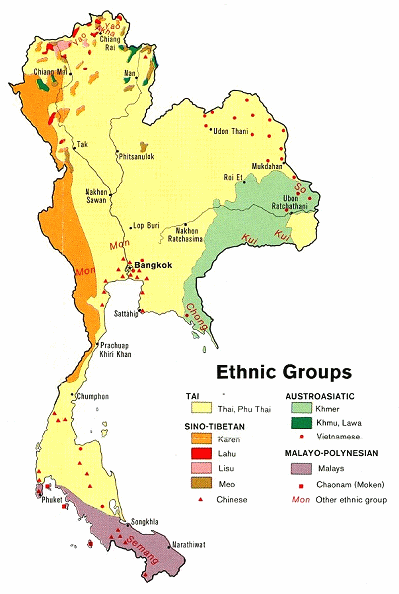
Map of
Thailand indicating the hill tribes ethnic
groups [45]
North Thailand:
-- red: Lahu (Muso, มูเซอ)
-- pink: Lisu
-- brown: Meo (Hmong)
-- orange: Karen (Kayin, Karian)
-- dark green: Khmu, Lawa
-- in red writing: Akha, Yao (Mien)
Central Thailand:
-- bright green: Khmer
-- red spots: Vietnamese
-- red triangles: Chinese
-- in red writing: Mon, So, Kui, Chong
Southern Thailand:
-- violet: Malays
-- red spots: Vietnamese
-- red triangles: Chinese
-- in red writing: Semang
|
For two or three decades, large numbers of girls from
north and north-eastern Thailand have been leaving home to
work in the sex industry. Girls and their families
understand the mechanics of the industry and most know how
to manage their careers. So much so that brothel keepers
[women mama-sans] began to think that ethnic Thai women
were a little too assertive [positive] to be good for
business. [Ethnic Thai girls were doing the minimum for
receiving a maximum so customers did not come any more, or
the girls developed even private strategies without the
brothel owner]. Their answer [of the brothel owners,
mostly women mama-sans] was to look for a new source of
recruits, and they found a ready supply in the hill (p.48)
tribes of northern Thailand. These are groups that the
development process has barely touched. They are people
who are on the fringes of Thai society - ethnically,
culturally, politically and economically. Many of these
peoples do not even live within the territorial limits of
a single state but customarily move backwards and forwards
through the jungles that span the Thai-Burmese border.
Their cultures are being undermined by the dominant
culture of the Thai state and their cultural and economic
integrity is increasingly fragile.
The sex industry targeted girls from these communities
because they were vulnerable individuals in the midst of a
vulnerable people [just promising good jobs "in the
city"]. Until recently girls from hill tribes did not even
attend school. They lived in families that were wracked by
poverty and in which there was a high rate of
underemployment and drug addiction. [Thai government let
them degenerate without speaking and attending anything.
And one can imagine where the human traffickers are coming
from...].
The exploitation of tribal girls was so blatant [obvious],
and so abhorrent [terrible], that both Thai government
agencies and non-governmental organizations stepped in to
try and stem the flow of girls to the brothels. They
established programs to identify and help the most
vulnerable girls by giving them protection, education and
some vocational training. Campaigns were also started in
the communities to raise awareness of the dangers posed to
young girls who left their tribes. This had the positive
effect of at least moderating the exodus to Thailand's
brothels. But there is one thing about the sex industry
that is very, very clear: it is always one or even two
steps ahead of those seeking to control it.
[Brothel keepers in Thailand? - Are mostly women!
They are mostly Thai WOMEN manipulating the girls and
young women for being offered to the Thai men! And in the
tourist centers of Thailand like Pattaya and Phuket many
brothel keepers in Thailand are right radical racist Swiss
from Switzerland. And now one has to know: Thai government
in Bangkok is not only racist against foreigners calling
them with the downgrading word "falang", but every ethnic
minority in Thailand has an own history how they became a
minority and Thai government often is not present at all
because they speak other languages...]:
|
Supplement: Read about ethnic
minorities in northern Thailand and it's
neighboring countries - sometimes with striking
stories
Thai Lahu mountain tribe
Lahu live in China ( 拉祜族) in Yunnan Province
(720,000); they also live in Thailand (ลาหู่)
where they are also called "Muso" ( มูเซอ), meaning
"hunter"; and Lahu live also in Vietnam
(La Hủ) mostly in Lai Chau province. Some Lahu
were lured to collaborate with the criminal
"U.S.A." during Vietnam war in Laos and after 1975
they had to fly to Thailand as refugees. Some
thousand Lahu even changed to criminal "U.S.A." as
refugees with a center in Visalia in California
[web06].
 [46]  [47]  [48]
Thailand, Lahu village [46] - Thailand, Lahu
music and dance group [47] - Thailand, Lahu
music performence [48]
Thai Lisu mountain tribe
Lisu people live in the
mountains of Burma (Myanmar) with 450,000; in
Southwest China in poor Yunnan Province with about
730,000; in Thailand with approximately 55,000 in
remote country areas, and in India in Arunachal
Pradesh [web07].
 [49]  [50]  [51]
Thailand, Lisu village [49] - Thailand, children
in a Lisu village at the Thai Burmese border
rolling down the hill [50] - Thailand, children of
a Lisu village in traditional suit [51]
Thai Meo (Hmong) mountain tribe
Hmong hill tribe (Vietnamese:
Mẹo) are living in mountain forest regions of
Laos, Vietnam, and Thailand. In China they are
included to Miao nationality. In China there are
more than 9 million, in Vietnam 787,600 (1999), in
Laos 450,000 (2005), in Thailand 150,000, in
Myanmar less than in Thailand; in criminal
"U.S.A." there are according to a census 186,310
(2000), the real figure is estimated to 250,000 to
300,000; in France there are 15,000, in Australia
2,000, in French Guayana 1,500, in Canada 600, in
Argentina 100 [web08].
 [52]  [53]  [54]
Thailand, Meo (Hmong) village [52] - Thailand, Meo
(Hmong) girl in traditional clothes and with a red
umbrella [53] - Hmong refugee camp Huay Nam
Khao in Petchabun Province, Thailand [54]
Meo (Hmong) in Thailand
<There are two subgroups of Hmong in
Thailand; the Blue Hmong and White Hmong.
Blue Hmong villages are located on high
mountain areas north from Doi Inthanon to
the Burmese border. They are the closest group to
Chiang Mai, with villages in the Doi Suthep -
Doi Pui National Park area.> Houses are in
clusters. People is organized in clans. They have
their own spirits and souls and rituals. Every
village has a shaman for exorcism of evil spirits
and restoring health. Typical clothes are made of
hemp and have blue and white batik patterns: <The
pleated skirts made of hemp died with blue and white
batik patterns make the Blue Hmong women
clearly identifiable. The women's jackets are made
of black cloth decorated with elaborate embroidery
for which the Hmong women are renown.
Men's clothes are also made of loose-fitting black
material, with embroidery on the jackets. The Hmong
use silver both for adornment and as a show of
wealth.> [web09]
 [55]  [56]  [57]  [58]
Laos, two Meo (Hmong) women in traditional clothes
at new years celebration in Nasala [55] - Laos,
Meo (Hmong) shaman [56] - book "The Hmong and
their stories" [57] - Meo (Hmong) children with
black and blond hair, nobody knows why [58]
Meo (Hmong) in Laos
during Vietnam wars 1945-1975 - flight and
suppression since 1975
Also Meo (Hmong) were lured to fight for European
colonialists against Vietnam, first since 1945
already under racist French commanders with up to
40,000 soldiers under the command of 400 French
officers. As a payment for this operation Hmong
were selling opium to the French forces then this
opium was sold in the "First World" by secret
transports (Operation X) [web08]. Criminal
"U.S.A." with it's criminal secret service "CIA"
followed operating in Laos (which officially was
"neutral") manipulating Meo (Hmong) people
fighting Vietnamese in the 1960s. In 1961 there
were 9,000 Hmong fighting against Vietnamese
forces under CIA command, since 1963 29,000 Hmong,
all in all during Vietnam war about 30,000.
Criminal CIA was often ordering rescue operations
for criminal "American" pilots [Agent Orange
poison actions] provoking heavy losses for Hmong
troop units. Meo (Hmong) troops had 10 times more
losses than "American" troops. During Vietnam War
Meo (Hmong) population was reduced by about 1/3
[web08].
|
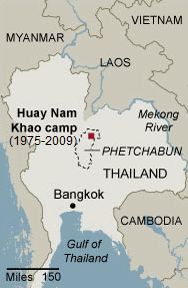
Map, refugee
camp "Huay Nam Khao" of the Meo
(Hmong) in Thailand 1975-2009 [59]
|
|
After criminal "U.S." troops left Laos in 1973
breaking the promise to bring the Hmong to
"U.S.A." they left them in Laos and Vietcong
killing actions began against Meo (Hmong) [web12].
In the following time and after "U.S." defeat in
1975 [because Vietnam never wanted to be parted
like Germany and Korea were parted] surviving Meo
(Hmong) collaborators had to fly to Thailand and
to the "U.S.A." [web10]. "U.S.A." let Hmong
refugees in since December 1975 [web12]. In
Thailand there was a refugee camp ("Huay Nam Khao"
[web08]) around a Thai temple in central Thailand
in the Thai province of Phetchabun [web10]. Other
Meo (Hmong) remained in Laos and are poor and
suppressed until today [web08]. In Thailand no
asylum was given to the Hmong refugees and they
remained without nationality and without passports
[web08]. In 2004 criminal "U.S.A." took 14,000 of
them [web10] mainly to California to Fresno and
Merced, and to Minnesota to St Paul [web08]. Since
2005 Thai police around the refugee camp
instructed the Thai population not to give
assistance to the Laotian Hmong refugees any more.
Thai police started also with arrests of Hmong
refugees who were found outside of the camp
visiting people or festivities [web13]. In 2006
Thailand wanted to send the Laotian Hmong refugees
already back to Laos but Laotian government
rejected the project stating that these Hmong
refugees in Thailand would not be Laotian citizens
and all would be a Thai problem. Thus Laos was put
under international control [web13]. In May 2008 a
fire in the refugee camp destroyed 100s of huts,
perhaps this was a maneuver of the refugees
[web15]. In June 2008 about 4,000 of the Hmong
refugees organized a march to Bangkok [web14]
which was intercepted by Thai police followed with
the detention of up to 600 Hmong refugees and some
of the leaders were deported back to Laos [web15].
At this time in June 2008 many Hmong were yet
persecuted in Laos: <For in Laos some Hmong
groups are being mercilessly hunted on account of
their link with former Hmong fighters, who during
the Vietnam war more than 30 years ago were
recruited by the American CIA as mercenaries
[payed soldiers]. More than 10,000 Hmong, among
them being many children, young people and women,
still have to remain in hiding in the jungle from
the Laotian and Vietnamese military.> [web14]
Thai police simply indicated that these Laotian
refugees wanted asylum for getting a Thai passport
for traveling to rich countries, so they would be
"economic migrants" [web15]. In December 2009 Thai
government was transporting the rest of 4,351
ethnic Hmong to the Laos border. Asylum petitions
were not possible [web10] and the suppression of
Meo (Hmong) in Laos is continuing without end
[web08]. <Lao government has denied they will
face retribution [revenge], and the Thai
government argues that the majority of the group
are illegal economic refugees.> [web11]
[There are no indications about trafficking gangs
luring girls or young women with jobs "in the
city", and there are no indications how the Hmong
are living in Laos now].
Thai Karen (Kayin, Kariang) mountain population
Thailand
The word "Karen" comes from
English colonialist administration. In Burma they
call themselves "Kayin", in central Thailand
"Kariang", and in northern Thailand "Yang"
[web16]. Padaung (Kekawngdu, Kayan) is a sub group
of Karen population [web17]. All in all they speak
15 languages. Karen population is parted between
Myanmar (Burma) and Thailand. In Thailand are
living about 400,000 Karen. Thai administration
makes a difference between Karen who have
emigrated since 17th century, and other Karen
emigrating after military atrocities in Burma
since 1984. The foundation of an own Karen state
was not successful but Myanmar army forces
attacked the military positions since the 1970s
provoking temporal streams of refugees in
Thailand, and since 1984 Karen territory was more
and more occupied constantly by Burmese army
forces committing mass murder, forced labor and
mass violation provoking 100,000s of Karen
refugees in Thailand, 50% of them in refugee
camps. Nobody wants to give them asylum. Even more
Karen are hiding in forests or are refugees in
Myanmar itself [web16].
 [60]  [61]  [62]
Karen hill tribe, long neck woman [60] - Thailand,
Karen / Karian woman weaving [61] - Karen village
at Thai Burmese border [62]
Khmu hill tribe in
Thailand
Khmu (Thai: ขมุ) are also called "Kammu",
"Khamu" or "Kemu", Vietnamese: Khơ Mú, Lao: ຂະມຸ
[kʰámū];
there are over 500,000 Khmu in the world,
450,000 of them in Laos (north and center,
second largest ethnicity), 43,000 in Vietnam,
10,000 in Thailand (near the Thai-Laotian
border, isolated villages partly without
electricity yet), 10,000 in China (southwest
China in Sipsong Panna in Yunnan Province, but
nor recognized ethnic group), 8,000 in criminal
"U.S.A." in Richmond in California coming as
refugees from Vietnam War. Some Khmu are also
living in Myanmar (former Burma) [web18].
Khmu in northern Thailand <live alongside the
Hmong and other regional minority ethnic groups.
Most Khmu in Thailand arrived recently from Laos
and Vietnam as refugees, also around the outset
of the Vietnam War.> [web18]. Khmu practice
magic and believe in spirits [web19].
 [63]  [64]  [65]
Khmu woman [63] - Thailand, Khmu festivity
with music and dance in traditional clothes in
the village of Ban Chom Ong [64] - Laos, Khmu
village of Ban Sam Yord [65]
Lawa [laua] hill tribe
in Thailand
Well, this map is not indicating the same
locations as "Lawa" locations than the first
big map. Lawa (stressing the second
sillable; in Thai ลั๊วะ or ละว้า),
in Lao ລະວ້າ, have many names:
T'in, Chao Dol, H'tin, Katin, Kha Che, Kha
Pai, Kha Phai, Kha T'in, Lua, Lwa, Mai, Mal,
P'ai, Phai, Praj, Pral, P'u Pai, Thin, Tie
und Tin [web20]. The main part of Lawa are
living in Laos [web21]. In China Lawa are a
sub group of Va nationality. Other Lawa
groups are also in Myanmar [web20]. All in
all are about 17,000 estimated [web21]. Life
is archaic and belief is animistic [web20].
Lawa people were driven away by the
immigrating Thai [web21]. Not married women
have white shirts with red bracelet, and
married women have multi colored clothes
[web20].
From 5th to 10th century Lawa were living
with the Mon also in today's central
Thailand before Thai ethnic group drove the
Lawa away. The local name of Lopburi comes
alledgedly from "Lawaburi" which was the
capital of Lavo Kingdom. Also the valleys of
northern Thailand were populated by the Lawa
before Tais came. First city of Wiang
Nophaburi is today's Chiang Mai [web21].
Lawa in Thailand are about 14,000 with rice
terrace agriculture living in the southern
part of Mae Hong Sorn province and on Bo
Luang high plain in southern Chiang Mai
Province [web22].
 [67]  [68]  [69]
Thailand, Lawa girl weaving in the region
of Chian Mai [67] - Thailand, Lawa men
with flute and women aside [68] - Lawa
village in Thailand [69]
Akha hill tribe in
Thailand
Akha (also called "Aka" or in Thai "Ai
Ko", in Laotian "Lao Sung") came from
Tibet over Burma and Yunnan in China.
Today they live in northern Thailand,
Laos and in Vietnam (called "Hà Nhì",
17,500). There are estimated in
Thailand, Laos, and Vietnam over 400,000
Akha totally. Additionally there are
almost 1.7 million in China called Hani.
In Thailand they live in height from
1,000 meters upwards in the provinces of
Chiang Rai, Chiang Mai, Lampang, Phrae
Tak and Kamphaeng Phet in bamboo houses.
Estimations of 2000 say there are about
50,000 Akha in 300 villages in Thailand.
Migration to Thailand is going on.
Agriculture is varied and also with
cuttle, and in some remote villages also
opium is consumed and opium is applied
for healing procedures. Manh Akhas in
Thailand have no passports yet and are
suppressed by police and military forces
[web23].
 [70]
 [71]
 [72]
Thailand, Akha bamboo house [70] -
Thailand, Akha girl with thread game
[71] - Thailand, old Akha woman near
Chiang Rai [72]
Yao hill tribe
in Thailand
Yao hill tribe is a big group with
it's center in south and southwest
China (in 2010 census 2 million and
796,003; Yao also live in northern
Laos, northern Vietnam, northern
Thailand (about 60,000) [web24] also
called "Mien" or Pau Yut (Pow Yout)
[web27]. There are over 34,000 Mien
living in 173 villages in North
Thailand [web26]. Yao also live in
northern Myanmar. Yao in Thailand
also call themselves as "Mien" or
"lu-Mien" as a sub group of the Yao
of China; in Vietnam they are also
called "Dao", Dzao, Zao, and "Red
Dzao" also as a sub group. First Yao
tribes had Taoism, today Buddhism
and a certain "Jesus" [web24]
because they are victims of
"missions" [web26].
 [73]
 [74]
 [75]
Thailand, Yao of Doi Mae Salong
[73] - Thailand, Yao / Mien woman
knitting [74] - Thailand, Yao /
Mien village [75]
And also Yao hill tribe (in Thailand
called "Mien") were abused by
criminal "U.S.A." for the useless
fight against Vietnam:
<Many Mien American elders fought
alongside the United States CIA
during the "Secret War" of Laos in
an effort to block weapon trails to
Vietnam. When the American operation
pulled out in 1975, hundreds of
families were forced to seek refuge
in the neighboring country of
Thailand. Hundreds died during this
heart-breaking journey on foot
through the deep jungles of
Southeast Asia. In the next few
years, thousands settled in Thailand
refugee camps awaiting uncertain
fate. Through programs from the
United Nations, roughly 60,000 were
sponsored to western countries such
as the United States. Approximately
50,000 Mien settled along the
western coast of the U.S. in states
of Washington, Oregon and
California. Approximately 10,000
settled in other parts of the
country, in states of Alabama,
Tennessee, Michigan, Illinois and
other states. This ethnicity group
has yet to be included in the United
States Census and consequently,
current population numbers have been
skewed anywhere from 50,000 to
150,000. Since resettlement in
America, historical contacts have
been and continue to be made,
between Mien Americans and Mien in
China and Vietnam. Many Mien
American relatives still remain in
the countries of Laos and
Thailand.> [web25]
|
|
Girls from Burma,
China and Cambodia for local Thai brothels -
illiterate Burma girls from 'Yai Thai' community
|
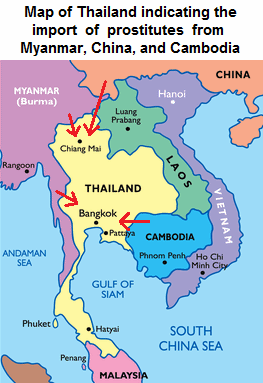
Map of Thailand
importing prostitutes from Burma, China,
and Cambodia [76]
|
|
A new set of recruits had been found in women from Burma
and to a lesser extent from southern China and Cambodia.
They were cheap and plentiful and, in the case of the
Burmese, they also appeared to be willing. Consequently
the number of sex workers in the Thai industry who
originate from the north of the country has been
decreasing in line with a corresponding increase in the
number of girls from other countries. Five to ten years
ago around half of the women working in the brothels of
Chiang Mai in northern Thailand were from Burma. Now
[estate 2000] 100% of brothel-based prostitutes are
Burmese [36].
[36] Interview with Jackie Pollock, EMPOWER, Chiang Mai,
Thailand
These women, especially from the (p.49)
'Yai Thai' community, are in demand for their white skin
and their delicate features. All of these girls are
illiterate.
Woman trafficking from Yunnan Province (China) to
Thailand's brothels
Yunnan is a peripheral and mountainous region of China.
Its people have a low standard of living by Chinese
standards, and educational levels and general statistics
on human development lay far behind the rest of the
country. What makes Yunnan a recruiting ground for the sex
industry is its proximity to Thailand with its
ever-expanding demand for fresh young bodies. Since the
1990s thousands of young women from tribal communities in
the Yunnan-Burmese border area have been trafficked to
Thailand [37].
[37] Kritaya Archavanitkul: Trafficking in Children for
Labor Exploitation including Child Prostitution in the
Mekong Delta (Bangkok: Institute for Population and Social
Research, Mahidol University, ILO-IPEC, July 1998), p.34
According to official figures, which may well be an
underestimation, around 2,500 women were trafficked out of
Yunnan in 1995 alone [38].
[38] Mr He Zhixiong, Yunnan Academy of Social Sciences,
speaking at a seminar in Mae Sai, Thailand, November 1997
Their main destinations were the Chinese marriage market
[in rich parts of China] and the brothels of Thailand.
Women coming from Burma to Thailand's brothels -
workers from Burma with Burmese prostitutes following
them
Burma's bitter history of civil war and political
repression by an authoritarian military government has
left hundreds of thousands of people displaced from their
homes and millions living in fear and appalling [dreadful]
poverty. It is a dream for agents of the sex industry.
There are thousands of young women without a home or a
livelihood who are desperate to escape the depredations
[plundering] of the Burmese army. They have an unenviable
choice. As one Burmese prostitute working in Thailand
stated, 'Why should we stay in Burma to be raped by
soldiers? If we come to Thailand we get raped as well, but
here we get paid for sex - at least most of the time.' The
refugee camps along the Thai-Burmese border are major
recruiting grounds for prostitutes [39]
[39] Archavanitkul: Trafficking in Children, p.28
and the estimated two million people who have migrated
from Burma into the surrounding countries since the early
1980s have formed an army of cheap male migrant laborers
and the prostitutes who service them [40].
[40] Archavanitkul: Trafficking in Children, p.3
Thailand is a 'promised land' or a 'hell' for
prostitutes
The attractions of working in Thailand are obvious for
young Burmese women. When you first cross the border from
Thailand into Burma there is little difference in the
infrastructure of buildings and roads. But there is a
palpable sense of desperation. Ten miles (p.50)
into Burmese territory, however, and the poverty is
shocking and inescapable. From the Burmese mountains
overlooking the border with northern Thailand, you can see
neatly cultivated fields, modern towns and roads that lead
south. To the poor, and those who have lost faith in their
country's future, it must seem like the Promised Land. For
some women it will be just such a Promised Land and for
many others it will be a hell.
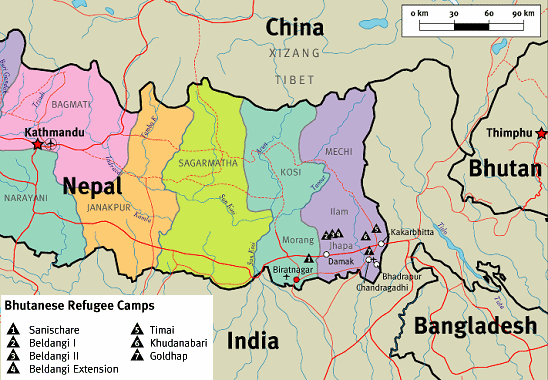
Women trafficking: girls from refugee camps in Nepal
|
|
|
Map of
Bhutan and Nepal with the refugee camps in
eastern Nepal [77]
|
It is a similar story for the dispossessed [expelled]
everywhere. They have little to fight with and few people
to fight for them. The networks that supply the sex
industry hover around these people. They hover, for
instance, around the one hundred thousand people of Nepali
ethnic origin who were expelled from Bhutan in the early
1990s in one of the world's lesser known chapters of
ethnic cleansing. Today [estate 2000] these people
languish [suffer] in refugee camps in the east of Nepal.
These people do not have permanent homes and they do not
have a nationality. They are of little interest to anyone.
Except, of course, the agents of the sex industry.

Nepal refugee camp in 2008 [78]
Ethnic minorities and tribal peoples form an excellent
recruitment pool for the sex industry because women's
status in many of these communities is not quite as
circumscribed as in the dominant national cultures. Women
have greater economic power, more social standing and
there are looser restrictions on sexual morality. Among
the Tamangs of Nepal, for instance, there is no taboo on
premarital sex. And in many of the poor farming
communities of northern Thailand, the country's obsession
with chastity and virginity does not have the same kind of
resonance as it does among the middle and upper classes.
This does not imply, however, that prostitution of girls
from these communities is accepted as a customary norm.
Ironically, the higher status of women in these societies
and their greater freedom of movement rebounds to their
cost because it means that the sex industry and its
clients can manipulate this freedom and profit from it as
a result of the communities' relative poverty. It is yet
another example of the global truth that (p.51)
mainstream cultures twist [block] and exploit
minority cultures to their own advantage.
Women trafficking: girls from slums and from
poor villages
Poor urban slums are increasingly profitable
recruiting grounds for the sex industry. Even so [but],
most brothel-based prostitutes and streetwalkers have
arrived in the city from the villages. There are
many ways in which girls migrate to the cities and there
are many means of trafficking.
[There comes a woman in beautiful clothes and with
beautiful jewelry promising good jobs "in the city"
bringing the girls and young women to the brothels which
are run by WOMEN mama-sans torturing, manipulating and
extorting the victims for years in a sex slavery which is
run mostly by WOMEN. Mostly women are committing the
crimes, and mostly women are trafficking women offering
them to men at the end].
Women trafficking: feminization of migration not only
for sex business
The 1980s and 1990s have seen a feminization of migration
throughout the world. In Asia this is a reflection of
greater opportunities for women and well as their greater
poverty. Crucially, in a social context in which women are
viewed as either the possessions of men or as some
collection of body parts for the use of the [...]ny, this
feminization of migration has left millions of women at
risk of sexual abuse and general economic exploitation.
The girls trafficked for prostitution are only the most
exploited of many exploited women.
Trafficked prostitutes say: their families sent them -
families say: the daughter has a job in a factory or as
a domestic servant - or know about sex work - but they
have no idea of sex slavery
Girls and women in prostitution frequently relate [tell]
similar stories about the background to their work. They
say that their families sent them or at least gave them
permission to leave home. Families waved them off happy in
the knowledge that their girl was going to the big city to
get a job in a factory or as a domestic servant. Many
families are not dissembling. They really think that their
child will have a better life away from the poverty of the
village. But it is hard to believe that all are so
ignorant of the fate that will befall their daughters.
In northern and north-eastern Thailand, in parts of Nepal,
Indonesia, China, Burma and India, families know that
their daughters will become sex workers. Perhaps they do
not understand the full implications of what this job will
involve. Some families honestly believe that it is 'easy
money' and they have a false idea of the conditions their
daughters will endure. However, they do know that she will
not simply be a waitress, or a dancer, or a maid in a rich
person's house. The trafficking of girls is on too large a
scale for it to be ignored and unnoticed.
In some cases families pretend not to (p.52)
know in order to spare themselves the shame of sending a
girl into prostitution. But be sure that for many -
perhaps the majority - it is unspoken knowledge. Gossip
travels fast even in the remotest villages of the Nepali
Himalayas, and few will be totally unaware of what happens
to girls who go to Mumbai.
Trafficking of women: 'Thai country women' - and the
Thai country families waiting for the money
The market for sex has made daughters a valuable commodity
in some poor communities. A Thai official in a
non-governmental organization (NGO) explained, 'What it
comes down to is that Thai country women are just another
kind of crop.' [41]
[41] International Movement Against All Forms of
Discrimination and Racism: Trafficking in Women in Asia: A
Reference Manual for Public Officials and Private Citizens
(Tokyo, undated), p.12
In northern Thailand a family with several daughters is
considered lucky, and a community leader in Riom Mon in
Chiang Mai province complains that 'some parents remain
idle, just waiting for money from their daughters'. [42]
[42] Skrobanek: Traffic in Women, p.74
Trafficking of women: birth of daughters is welcome now
in Nepal and in India's prostitute castes
Just as in Nepal and in India's prostitute castes, the
birth of a daughter here is no longer a cause for lament.
Sex work has given them a market value [43].
[43] Than-Dam Truong: Sex, Money and Morality, p.74
Thailand: teen girls sent from provinces of Chiang Mai
and Chiang Rai - money comes to the provinces - the girl
is 'successful'
|

Thailand, Chian Mai, brothel
line [x001]
|
|
Report
about Chiang Mai from May 2010
<Fear of 'letting down' the trafficker or
pimp is high and image is everything. As you
walk down the street, you know that you're being
watched. Having Emmi there was very insightful.
She told us what was being said in Thai that the
foreigners (mainly middle-aged men) are
oblivious to. On this street you can buy sex for
as little as £4. For £10 you'll get whatever you
want for the whole night.> [web35]
|
|
|
|
|
|
Men
traffickers are controlling the area, the
streets, the brothels and the customers.
They are urging children for selling
flowers and they destroy any feeling of
joy but are provoking depression in the
eyes of the women and in the heart of the
customers - in the name of Thailand's sex
industry [web35]. |
Sending girls into prostitution, usually when they are
between thirteen and nineteen, is not considered to be
shameful in provinces of northern Thailand like Chiang Mai
and Chiang Rai [44].
[44] I am indebted to Sompop Jantraka of the Daughters'
Education Programme Mae Sai for his observations on these
points.
The whole community accepts sex work - and this includes
officials and religious organizations because, ultimately,
they all benefit financially from the trade. Evidence from
Thailand, Nepal and Indonesia, among other places,
suggests that a change in attitudes towards prostitution
occurs after the women from a poor community have been
involved in the business for a number of years. First
there is the demonstration effect: girls return to poor
villages with some money. Providing the money is
substantial enough - and in a poor community it need only
be a modest sum - the girl's shame is ignored because she
has been successful and her money eventually buys
her acceptance.
A crucial turning point comes when the daughters of former
prostitutes are sent to the city for sex work. It takes a
generation - perhaps two - and then prostitution becomes a
profession and a standard career 'choice' for girls from
poor communities who almost invariably have limited
education and minimal skills. This process (p.53)
has only occurred in pockets throughout Asia but the
phenomenon is spreading and a greater and greater number
of girls are being reared [educated] for prostitution.
Nepal: teen girls sent from Tamang tribe
Amongst the Tamangs of Nepal the trading of girls is an
open secret [45].
[45] Report: Girl Trafficking in Sindhupalchowk: A
Situation Analysis Report on Mahankal and Inchowk Village
Development Committee (ABC Nepal, undated), p.6
There are virtually no girls between the ages of thirteen
and twenty in villages like Ichowk in Sindhupalchowk
[district] [46].
[46] Child Workers in Nepal (CWIN), 'The Road to Bombay';
In: Voices of Child Workers (Kathmandu, December 1992),
p.52
Supplement: brothel cages in
Mumbai brothel prisons

Brothels in Mumbai are sometimes organized putting
girls into brothel cages so they will serve men at
the end [79]
Read precisely what is done
with the young girls in brothel prisons in
Mumbai in India:
<Girls in a brothel in Faulkland road in the
red light area. There are currently estimated
20,000 prostitutes in Kamathipura, the majority
of which have been trafficked. The average age
of entry into Kamathipura is 12 (but its often
as young as 7). The girls who are trafficked,
especially the minors, become sex slaves. They
are usually held in the brothel 'cages' for 3-5
years, until they have been 'broken' and the
madams allow them to sell themselves openly on
the street, in front of the brothel houses. The
girls are still not free though and describe the
red light area as an open prison.> [web28]
May be Asia really has some sex problems?
|
|
Prostitute rate: 1 per family in northern Thailand and
northern Philippines - 1 girl per family is 'sacrificed'
Similarly in northern Thailand and parts of the
northern Philippines there are communities in which every
family has a prostituted daughter. Initially girls were
sold into the sex industry because families had few
alternatives. They were desperately poor and the selling
of a child made the difference between the rest of the
family going hungry and providing them with just enough to
eat. These girls were sacrificed so that others could
survive.
Teen prostitution
in Asia for 'a modern lifestyle' of the family - above
all in Thailand, with a 'deposit' in advance of the
girl trader (tok khieu)
In some parts of Asia this is still the case but in those
areas where prostitution is a career option for thirteen-
and fourteen-year-old girls there is a complicating
factor. Poor and marginal communities are besieged with
the values, images and the materialism of affluent society
and these disadvantaged groups have, inevitably, also
desired the same symbols of status. One way they can
afford at least some of the coveted [demanded] commodities
of a modern lifestyle is by trading a daughter into sexual
slavery.
In Thailand this has become a sophisticated system of
exchange. A customary practice known as tok khiew
[doog kiao]
(which means 'green harvest') has been adapted to the
needs of the sex trade. In the original version farmers
pledged their unharvested rice crop in return for a loan.
This system now also applies to girls. Agents place a kind
of deposit on girls of twelve and thirteen, and sometimes
even younger if they are exceptionally pretty and show
promise of maturing into attractive teenagers. In return
for this deposit the girl is pledged to the sex industry.
Thailand, study of 1990: 60% of Thai families sending
daughters to brothels just for 'consumer goods' - Thai
girls 'Go South'
A study was undertaken in 1990 with the aim of
establishing the reasons why some Thai families encouraged
their girls to become prostitutes. It came up with some
depressing conclusions. It found that 60% of families
sending daughters to the brothels were not (p.54)
forced to do so because of acute poverty. Instead they
were motivated by the desire to own consumer goods like
televisions and videos [47].
[47] Ecumenical Council on Third World Tourism: Caught in
Modern Slavery: Tourism and Child Prostitution in Asia
(Bangkok, 1992), p.41
There is competition among families to acquire household
items. In some ways this consumerism complements
traditional values which place a strong emphasis on
external appearance [48].
[48] Warunee Fongkaew: 'Sexuality and Gender Norms Among
Thai Teenagers'; paper presented at the regional workshop
on the social Sciences and Reproductive Health,
Karnchanaburi, Thailand, July 1996, p.3-4
All the young ethnic Thai girls who 'Go South' are not
dragged screaming to the brothels. Only rarely are they
held in captivity. Most would not claim to be forced or
coerced, but their options are so narrow, and they are so
young, that their compliance [to say yes] amounts to
coercion.
Parents are not solely to blame. The perpetrators of the
prostitution of young girls in places like Thailand are
not just individuals but are entire social, political and
economic systems. There is skewed [deformed] economic
development that leaves whole communities without access
to the fruits of modern society while at the same time
tempting them with its products. There is a social and
sexual system that reduces women's utility to sex. There
is a socialization process which conditions women to
accept that they must help their families by any means
possible. There are men who demand the right to buy
relationships of power with women and there is an industry
ready to organize and profit from this demand.
[Coward
Asien governments without jobs in the countryside - Thai
prostitutes shifted around also in Switzerland
Additionally Asian governments are excellent with racism
against the population in the countryside never installing
good jobs in the countryside thus the rural population is
only a poor mass being shifted around by the government.
In this situation prostitutino is automatically considered
as a "solution" in the economic disaster in Asia - and the
rich Asian racists in the town are meeting just the women
from the countryside in the brothels... Concerning Thaialnd many Thai brothel
owners are also Swiss men from Switzerland and they are
shifting Thai women also to Switzerland with their
connections to the secret service and to the migration
police. And in Switzerland "friends" are shifting them
from brothel to brothel. This can end well, but
sometimes also not so well].
Parents
and communities are only small-time traders in a much
larger pattern of commerce created by vast social, sexual,
economic and political forces.
[The
elements creating the conditions for a big sex business:
deliberately there are no good jobs in the countryside
The elements conditioning the big sex business are the
ministry for social affairs, police boards, economic
department and secret services. Thus there are
DELIBERATELY NO good jobs installed in the countryside so
always many young women are heading into the prostitution
business which is considered as a "salvation". This is how
racism of rich Asian men is working in Asia - and we
remember: "Pure" Asian women are sending wild husbands to
the brothel, and the houses in Asia are just built thus
the neighbors can peep all sexual action what the bride
and the bridegroom don't want. No further questions...!]
Example: Thai prostitute began massage work in Bangkok
with 14 years
I met a gorgeously beautiful woman in a Pattaya nightclub,
where she danced in a tiny bikini and sold sex to
foreigners. Once we had established that I did not want to
buy sex from her she told me about her career and how well
she had done for herself and her family.
<I am from northern Thailand. From a little village. We
were not rich but not poor. My mother was a sex worker in
Bangkok during the time of the Americans (during Vietnam
War). I have two sisters and one brother. When I was at
school I thought about getting a job in an office because
I was quite good at my studies but when I was fourteen I
(p.55)
started this work. My family said I could earn more money
this way. I went to Bangkok and I worked in a massage
parlor for a while but the work wasn't good: the clients
were not nice and the pay wasn't enough. I worked there
for three years until I paid off my debt. Because the
customers like me, and I give good service, I got a better
job in a bar and I entertained a lot of foreigners. One
time I went to Japan for a few months and I earned a lot
of money. This is good work for me because I can send
money to my family. My brother has a motorbike and perhaps
one day we can buy a car. My family has already made
another room in the house with the money I sent them. They
are very happy and proud that I am more successful than
other girls in my village.>
Nepali villages with families doing nothing but waiting
for the money of their prostituted sisters and daughters
As you walk through the villages of [mountain districts
of] Sindhupalchowk and Nuwakot in Nepal it is possible to
pick out the families of girls working in Indian brothels.
They have the houses with tin [metal] roofs and men
lolling [doing nothing] outside in the shade listening to
radios and playing cards. This relative affluence and
leisure is bought with the bodies of their sisters and
daughters.
[Just the same happens in the countryside in Thailand
but men are not playing cards there but they are mostly
wasting the money drinking beer and whiskey thus also men
are loosing any brain!]
Example: Nepali sisters being prostitutes in Mumbai
In the lanes of Kamatipura red light area in Mumbai, I met
a Nepali prostitute who looked around twenty-three but who
said she was thirty-five. She was confident and heavily
made-up. This is what she said:
<I am from Sindhupalchowk in Nepal. My sister is also
in the profession here. There are a lot of us from the
same place. I came here about ten years ago with a gharwali
(woman brothel manager) from my village.>
It was clear from this young woman's comments that she was
not physically coerced into prostitution and that she had
started her career as a prostitute when she was a child.
2.11: Successful prostitutes - sold children -
almost no or no education
General indications: successful prostitutes changing
social values: prostitution becomes a normal business
The mixture of poverty, successful prostitutes and
consumer (p.56)
culture has dramatically altered societal values about
prostitution in selected areas of Asia. But for most
people, in most communities, it remains an unacceptable
trade. This, however, cannot stop the desperately poor
from trying to sell their children and often succeeding in
the task.
[Writer Louise Brown is hiding all negative
effects of making prostitution business career
-- with alcohol abuse,
-- loosing brain and loosing memory capacity by alcohol
abuse,
-- and thus any further education is blocked by loss of
brain and memory capacity because alcohol has reduced the
brain and the memory
-- eventually there is also smoking without end,
-- loss of health because work is always during the night
and the immune system is weak
-- loss of health by sexual transmitted diseases and AIDS
illnesses
-- loss of the feminine voice getting a more male and low
voice by the high alcohol consumption in combination with
working during all nights.
Most of these points are never mentioned by Louise Brown.
Thus when somebody makes prostitution business it should be
only for 4 or 5 years not more saving the body].
|
|
|
Sold
virgins from poor families in Cambodia in
Mekong Delta - and in Indonesia [80] |
Sold virgins from
poor families in Cambodia in Mekong Delta - and in
Indonesia
Poor families in Cambodia are aware that they can demand,
and receive, a high price for their daughter's virginity
and daughters know that this is a way they can help their
families. In the Mekong Delta there are well-documented
cases in which parents directly or indirectly are involved
in selling children - some as young as twelve - into
prostitution [49].
[49] Archavanitkul: Trafficking in Children, p.69
It is still possible, though more unusual, to find similar
cases in Indonesia [50].
[50] Lin Lean Lim: The Sex Sector, p.49
Sold children from poor families in Bangladesh - and no
control
In the very poorest communities families are not even
anxious to secure a payment for their girls. In
Bangladesh, girls are taken from their families by [women]
agents [with beautiful clothes and jewelry on their hands]
who promise them jobs ["in the city"]. Some of these
parents and guardians are too poor to be choosy and
cautious about what kind of work their daughters will do.
As far as many are concerned they are happy to have girls
taken away because it relieves them of another mouth to
feed and another dowry to collect [51].
[51] In conversation with Salma Ali, Director of the
Bangladesh National Women Lawyers' Association, Dhaka,
Bangladesh
Prostituted girls and sold girls in South Asian
prostitution: low or no education levels
[To be illiterate means that a simple woman trafficker has
got power over the girl just because the girl cannot read
or write anything and is absolutely dependent on anything
what the woman trafficker is saying].
Many trafficked girls and those who are directly coerced
into prostitution in Asia share a similar set of
characteristics. First they have low educational levels.
In South-East Asia a report by the International Labor
Organization found that sex workers were less educated
than the average woman [52].
[52] Lin Lean Lim: the Sex Sector, p.3
In India, where most women are illiterate, brothel-based
prostitutes and streetwalkers almost invariably have
little or no schooling [53].
[53] UNICEF: A Situation Analysis, p.91
In Sonagachi, which is the biggest brothel in Calcutta,
only 15% of the women are literate [54].
[54] Department of Epidemiology, All India Institute of
Hygiene and Public Health: 'Assessment of the Sex Trade in
Calcutta and Howrah', undated, p.52
This pattern is repeated over and over again throughout
South Asia.
Sompop Jantraka: Education organization at Thai-Burmese
border - education and 'alternative employment'
Supplement: Sompop Jantraka - a
savior of children in brothel prisons
![Sompop Jantraka, portrait of a savior of
children in forced prostitution in brothel prisons
[criminal mafia dominated] Thailand Sompop Jantraka, portrait of a savior of
children in forced prostitution in brothel prisons
in [criminal mafia dominated] Thailand](02-d/081-Sompop-Jankatra-portrait.jpg)
Sompop
Jantraka, portrait of a savior of children in
forced prostitution
in brothel prisons in [criminal mafia dominated]
Thailand [81]
<Sompop Jantraka currently
is living in Mae Sai, a town in northern Thailand.
He is from Surat Thani in the south of Thailand
[near the Malaysian border]. As a kid he roamed
the streets and lived a life of poverty. “Sompop
wasn’t the kind of kid anyone expected to grow up
to be a hero.” (Horn, 2006, p. 1) It was not until
an American woman gave him the chance to get an
education and gave him the confidence and
knowledge that he could make something of himself
that his life found a purpose. Since then, he has
worked hard to do the same thing for other young
children.> [web29]
There should be more Sompop Jantrakas.
|
|
Sompop
Jantraka (a Thai activist saving girls from child
prostitution in Thailand from Thai brothel prisons
[web29]) runs the Daughters' Education Program in areas
along the Thai-Burmese border and works with girls who are
victims of trafficking for prostitution. His organization
tries to curtail [reduce] the trade in girls by
identifying those who are most likely to be trafficked.
The girls are provided with a basic education and a
training that might provide them with an alternative form
of (p.57)
employment. Those who are in imminent danger are given a
safe environment in which to stay. The program identifies
a number of common risk factors leading to trafficking and
prostitution, especially among the tribal communities. A
girl is more likely to be recruited into prostitution if
she has a sister or relative who is already in the
industry. She is especially vulnerable if alcoholism, drug
addiction, divorce or the death of a parent shakes the
structure of the family.
2.12: Conditions favoring prostitution: no
school, brute stepmothers, civil wars, famines, or a
volcano
Thailand:
education finishing after 12 or 13 - girls 'Go
South'
The point at which these factors come into play is when
the girl finishes compulsory education at the age of
twelve or thirteen. Freed from school, girls from
northern Thailand then 'Go South'. [Taboo topic of
alcoholism in prostitution work is never mentioned by
Louise Brown].
Family conditions for prostitution of the daughters:
girls in Calcutta in India - Hindu girls from Bengal
Problems within the family, and not simply poverty, are
the most important factors pushing girls into
prostitution. This is borne out [confirmed more and more],
time after time, by the experiences of women who were
forced into prostitution by economic necessity and by
girls who were trafficked and sold into prostitution. In
Calcutta, for example, trafficked girls are often between
twelve and fifteen years old. Trafficked Bengali Hindu
girls are commonly from families in which a parent has
died and the remaining parent has remarried. At this point
the girl becomes subject to abuse from her stepparent
within the reconstituted family.
Bengalen: discrimination of girls by stepmothers in
Bengali Muslim families - flight of girls - lost
girls sold to brothels - no money for marriage of girls
as a reason to send them into prostitution
Among Bengali Muslims the situation is slightly different.
Bengali Muslim men commonly have many wives and many
children whom they cannot support. Because children
usually remain with their fathers after a divorce, new
wives discriminate against the children of earlier wives.
Girls report that they ran away from home because they
could not tolerate the hunger and the beatings [55].
[55] I am grateful for discussions with Indrani Sinha and
the staff of Sanlaap, Calcutta, for this information
From there it is only a small step to being absorbed
within trafficking networks and sold to a brothel. A study
undertaken of prostitutes in Mumbai in 1962 discovered
that the death of a girl's guardians and ill treatment by
relations was the single most important factor pushing
females into prostitution [56].
[56] S.D. Punekar and Kamala Rao: A Study of Prostitution
in Bombay: With Reference to Family Background (Mumbai:
Lalvani Publishing House, 1962).
Almost forty years later the situation is remarkably
similar. In interviews with girls rescued in a 1996 raid
on Mumbai brothels it was found that over (p.59)
half of the girls had grown up in families in which one or
both parents had died. Their home life was also marked by
a collapse of family conventions. Some families, for
instance, lacked the capacity, or willingness, to arrange
a marriage for their girls [57].
Example: terror of stepmother - flight of the girl -
girl sold to Tanbazar brothel in Dhaka [capital of
Bangladesh]
The experience of a woman who was trafficked into the
Tanbazar brothel when she was twelve, and who now works on
the streets of Dhaka, is a common one throughout South
Asia.
<My mother died when I was little and my father
remarried. My stepmother was cruel to me and my brother,
but my brother was lucky and my maternal aunt said she
would look after him. I had to stay with my stepmother and
do all the chores [house work] and look after my little
half-brothers. She would beat me for no reason and would
not give me food so I was always very hungry. One day I
couldn't stand it any more so I ran away from the house. I
walked and walked because I had nowhere to go. I met a
woman on the road and she said she could find me a job in
the city. She seemed nice and kind and not like my
stepmother so I went with her and she sold me to a
brothel.>
Marriages fail and parents fail and, inevitably,
girls and women carry the heaviest burden as a result.
[More examples of terrorist stepmothers in
Bengal and India
Searching in the Internet a little bit one actually can find
horrible behavior of stepmothers in Bengal and in India
(search 2013):
-- burning a youth daughter because the daughter refused the
forced marriage and wanted to follow her school education,
news from 14 May 2013 [web30]
-- a stepmother strangulated a 3 years old child in
Jamshedpur in India at Mahatma Ghandi Memorial College (MGM
College), news from 12 April 2013 [web31]
-- a stepmother in Lucknow (India) is always discriminating
two children until the 12 years old boy is killing her with
the revolver of the father, news from 6 September 2012
[web32]
-- a stepmother in Delhi is always discriminating a
stepdaughter and the stepson is murdering the stepmother,
news from 7 March 2012 [web33].
It seems that women in India are not prepared well for being
second wives - emotional education seems to be missing. And
leaving such a family is even better than committing a
murder case. But in India and in Bengal the children rescue
homes are missing!
Thailand: order to the girls 'to support their parents'
by prostitution - after separation earn the support for
children
Sixty per cent of girls from northern Thailand enter
prostitution in order to support their parents. A majority
of Thai sex workers from the north-east do so after the
failure of a marriage and the subsequent need to support
their children [58].
[58] Lin Lean Lim: The Sex Sector, p. 147-149
|

|
|
Red
Khmer in Phnom Penh 1975 [82] |
Cambodia with
civil war provoking broken families - girls
helping with prostitution
It is the same story wherever you go. Cambodia has been
tortured by years of war and genocide [1970s and 1980s].
Basic familial relationships were irredeemably traumatized
during the Pol Pot regime, when children informed upon
their parents and parents upon their children. The
fundamental building blocks of Cambodian society were torn
apart as families unravelled. They have not yet recovered
[2000]. This legacy (p.59)
makes the sale of children, and the buying of people, that
much easier.
Troubled families are the breeding grounds for sex
workers. And troubled families in poor, marginal and
crisis-ridden communities generate the most reliable
supply of cheap girls. Civil wars and natural calamities
[catastrophes] produce bumper [special] harvests for the
sex industry.
Example of North Korea: famine provoking emigration and
woman trafficking for prostitution work in China
Famine-struck North Korea cannot feed its people. It
cannot feed the girls who flee across the Chinese border
in search of food and who are met by sex industry
enterpreneurs who take them to brothels in Chinese cities
[59].
Example of Philippines: mass evacuations by
volcano eruption and woman trafficking for prostitution
work
When [in 1991] Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines erupted
and displaced thousands of people from their homes, it was
the experienced [mostly women] agents of the sex industry
[in beautiful clothes and with jewelry offering jobs "in
the city"] who were some of the first to offer their
sympathy and their own variety of support in the centers
sheltering the victims. Like all successful business
people they had their eye on a bargain.
You don't believe? Here is the proof
for refugee camps after the Pinatubo explosion:
 [83] [83]  [84] [84]
Philippines, outbreak of volcano Pinatubo in 1991
[83] - Philippines, tent camp after the outbreak of
Pinatubo in 1991 [84]
Read precisely the text by Nigel Dickinsen:
<VOLCANO AFTERMATH, Philippines. Tent city
refugee camp.Central Luzon, Mount Pinatubo volcano
erupted in 1991 and caused massive destruction of
urban and rural landscape. Many indigenous Aeta
and Igorot people were displaced. White volcanic
ashes settled and disfigured the landscape. Many
live in ramshackle shelters, in refugee camps and
settlements, living on humanitarian aid.>
[web34]
When in such a poverty without any statal measure
for water and shower and job a nice woman in nice
clothes with jewelry on her hands comes offering
jobs "in the city", you would say no? The thing is
that a job trafficker needs a license and jobs
have to be controlled.
|
|
General indications:
prostitution exists because of a lost balance of
conditions - making money in emergency situations
Let us make no mistake, prostitution is not just about
poverty. It is a business founded upon all sorts of
inequalities. It is a business that is constructed out of
the distorted relations of power between men and women,
between the poor and the rich and between the minorities
and mainstream of a society. The sex industry makes money
because it buys cheap raw materials and packages them
well. It turns vulnerability into a commodity and that
commodity into a profit (p.60).
[Addition: There would be measures
Job advisers should be urged to have a license, and the jobs
where the people are brought must be controlled. As Asian
governments also like to visit brothels and as they like to
consume many young girlss and as they don't rate importante
European Human Rights - because those would come from former
colonialists - there is not much change concerning the
conditions against women in Asia. Concerning the position
against Human Rights Asia and Islam are just very
similar...]
<<
>>
[30]
[31]
[32]
[33]
[37]
[38]
[39]
[34]
[35]
[36]
[40]
[41]
[42]
[43]
[44]


[46]
[47]
[48]
[49]
[50]
[51]
[52]
[53]
[54]
[55]
[56]
[57]
[58]
[60]
[61]
[62]
[63]
[64]
[65]
[67]
[68]
[69]
[70]
[71]
[72]
[73]
[74]
[75]
[83]
[84]

![Sompop Jantraka, portrait of a savior of
children in forced prostitution in brothel
prisons in [criminal mafia dominated] Thailand Sompop
Jantraka, portrait of a savior of children in
forced prostitution in brothel prisons in
[criminal mafia dominated] Thailand](02-d/081-Sompop-Jankatra-portrait.jpg)